linux服务器 开发相关视频解析:
网络程序需要处理的第三类事件是定时事件,比如定期检测一个客户连接的活动状态。服务器程序通常管理着众多定时事件,因此有效组织定时事件,使之能在预期的时间点被触发且不影响服务器的主要逻辑。
将每个定时事件分别封装成定时器,并使用某种容器类数据结构,比如链表、排序链表和时间轮,将所有定时器串联起来,以实现对定时事件的统一管理。
定时
定时是指在一段时间之后触发某段代码的机制。Linux提供了三种定时方法:
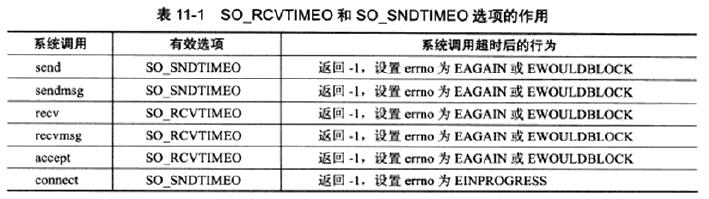
- socket选项SO_RCVTIMEO和SO_SNDTIMEO
- SIGALRM信号
- I/O复用系统调用的超时参数
socket选项SO_RCVTIMEO和SO_SNDTIMEO
socket选项SO_RCVTIMEO和SO_SNDTIMEO分别用来设置socket接收数据超时时间和发送数据超时时间。这两个选项仅对与数据接收和发送相关的 socket 专用系统调用有效,这些系统调用包括send、sendmsg、recv、recvmsg、accept和connect。可以根据系统调用的返回值以及errno来判断超时时间是否已到,进而决定是否开始处理定时任务。
1#include <sys/types.h>
2 #include <sys/socket.h>
3 #include <netinet/in.h>
4 #include <arpa/inet.h>
5 #include <stdlib.h>
6 #include <assert.h>
7 #include <stdio.h>
8 #include <errno.h>
9 #include <fcntl.h>
10 #include <unistd.h>
11 #include <string.h>
12 //超时连接函数
13 int timeout_connect(const char* ip, int port, int time);
14 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
15 {
16 if(argc <= 2)
17 {
18 printf("usage: %s ip_address port_number\n", basename(argv[0]));
19 return 1;
20 }
21 const char* ip = argv[1];
22 int port = atoi(argv[2]);
23 int sockfd = timeout_connect(ip,port,10);
24 if(sockfd < 0)
25 {
26 return 1;
27 }
28 return 0;
29 }
30 int timeout_connect(const char* ip, int port, int time)
31 {
32 int ret = 0;
33 struct sockaddr_in address;
34 bzero(&address,sizeof(address));
35 address.sin_family = AF_INET;
36 inet_pton(AF_INET,ip,&address.sin_addr);
37 address.sin_port = htons(port);
38 int sockfd = socket(PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
39 assert(sockfd>=0);
40 //通过选项SO_RCVTIMEO和SO_SNDTIMEO所设置的超时时间的类型是timeval,这和select系统
41 //调用的超时参数类型相同
42 struct timeval timeout;
43 timeout.tv_sec = time;
44 timeout.tv_usec = 0;
45 socklen_t len = sizeof(timeout);
46 ret = setsockopt(sockfd,SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDTIMEO, &timeout, len);
47 assert(ret!=-1);
48
49 ret = connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&address, sizeof(address));
50 if( ret == -1 )
51 {
52 //超时对应的错误号是EINPROGRESS
53 if(errno == EINPROGRESS)
54 {
55 printf("connecting timeout, process timeout logic\n");
56 return -1;
57 }
58 printf("error occur when connecting to server\n");
59 return -1;
60 }
61 return sockfd;
62 }
SIGALRM信号
由 alarm 和setitimer函数设置的实时闹钟一旦超时,将触发SIGALRM信号。我们可以利用该信号的信号处理函数来处理定时任务。但是,如果要处理多个定时任务,我们就需要不断地触发SIGALRM信号,并在其信号处理函数中执行到期的任务。一般而言,SIGALRM信号按照固定的频率生成,即由alarm或setitimer函数设置的定时周期T保持不变。如果某个定时任务的超时时间不是T的整数倍,那么它实际被执行的时间和预期的时间将略有偏差。因此定时周期T反映了定时的精度。
举例:
基于升序链表的定时器-》简单的定时器实现 添加定时器的时间复杂度是O(n),删除定时器的时间复杂度是O(1),执行定时任务的时间复杂度是O(1)
定时器通常至少要包含两个成员:一个超时时间(相对时间或绝对时间)和一个任务回调函数。有时候还可能包含 回调函数 被执行时需要传入的参数,以及是否重启定时器等信息。
服务器程序通常要定期处理非活动连接:给客户端发一个重连请求,或者关闭该连接,或者其他。Linux在内核中提供了对连接是否处于活动状态的定期检查机制,我们可以通过socket选项KEEPALIVE来激活它。不过使用这种方式将使得应用程序对连接的管理变得复杂。因此,考虑在应用层实现类似于KEEPALIVE的机制,以管理所有长时间处于非活动状态的连接。
利用alarm函数周期性地触发SIGALRM信号,该信号的信号处理函数利用管道通知主循环执行定时器链表上的定时任务-关闭非活动的连接。
timelink.h
1 #ifndef LST_TIMER
2 #define LST_TIMER
3
4 #include <time.h>
5 #define BUFFER_SIZE 64
6 class util_timer; //前向声明
7
8 //用户数据结构:客户端socket地址、socket文件描述符、读缓存和定时器
9 struct client_data
10 {
11 sockaddr_in address;
12 int sockfd;
13 char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
14 util_timer* timer;
15 };
16
17 //定时器类
18 class util_timer
19 {
20 public:
21 util_timer():prev(NULL),next(NULL){}
22
23 time_t expire; //任务的超时时间,这里使用绝对时间
24 void (*cb_func)(client_data*); //任务回调函数,输入参数是客户数据
25 client_data* user_data; //指向用户数据
26 util_timer* prev; //指向前一个定时器
27 util_timer* next; //指向下一个定时器
28 };
29
30 //定时器 链表 ,它是一个升序、双向链表,且带有头结点和尾结点
31 class sort_timer_lst
32 {
33 public:
34 sort_timer_lst():head(NULL),tail(NULL){}
35 ~sort_timer_lst()
36 {
37 util_timer* tmp = head;
38 while(tmp)
39 {
40 head = tmp->next;
41 delete tmp;
42 tmp = head;
43 }
44 }
45
46 //将目标定时器timer添加到链表中
47 void add_timer(util_timer* timer)
48 {
49 if(!timer)
50 {
51 return;
52 }
53 if(!head)
54 {
55 head = tail = timer;
56 return;
57 }
58 //如果目标定时器的超时时间小于当前链表中所有定时器的超时时间,则把该定时器插
入链表头部
59 if(timer->expire < head->expire)
60 {
61 timer->next = head;
62 head->prev = timer;
63 head = timer;
64 return;
65 }
66 add_timer(timer,head);
67 }
68
69
70 //当某个定时任务发生变化时,调整对应的定时器在链表中的位置
71 //这个函数只考虑被调整的定时器的超时时间延长的情况
72 void adjust_timer(util_timer* timer)
73 {
74 if(!timer)
75 {
76 return;
77 }
78 util_timer* tmp = timer->next;
79 //如果被调整的目标定时器在链表尾部,或者该定时器新的超时值仍然小于下一个定时
器超时值,则不用调整
80 if(!tmp||(timer->expire < tmp->expire))
81 {
82 return;
83 }
84 //如果目标定时器是链表的头结点,则将该定时器从链表中取出并重新插入链表
85 if(timer == head)
86 {
87 head = head->next;
88 head->prev = NULL;
89 timer->next = NULL;
90 add_timer(timer,head);
91 }else{
92 //如果目标定时器不是链表的头结点,则将该定时器从链表中取出,然后插入其原来所
在位置之后的部分链表
93 timer->prev->next = timer->next;
94 timer->next->prev = timer->prev;
95 add_timer(timer,timer->next);
96 }
97 }
98
99 //将目标定时器从链表中删除
100 void del_timer(util_timer* timer)
101 {
102 if(!timer)
103 {
104 return;
105 }
106 //链表中只有一个定时器
107 if((timer == head)&&(timer == tail))
108 {
109 delete timer;
110 head = NULL;
111 tail = NULL;
112 return;
113 }
114 //如果链表中至少有两个定时器,且目标定时器是链表头结点
115 if(timer==head)
116 {
117 head = head->next;
118 head->prev = NULL;
119 delete timer;
120 return;
121 }
122 //如果链表中至少有两个定时器,且目标定时器是链表的尾结点
123 if(timer==tail)
124 {
125 tail = tail->prev;
126 tail->next = NULL;
127 delete timer;
128 return;
129 }
130 //如果目标定时器位于链表的中间
131 timer->prev->next = timer->next;
132 timer->next->prev = timer->prev;
133 delete timer;
134 }
135
136 //SIGALRM信号每次被触发就在其信号处理哈桑农户中执行一次tick函数,以处理链表上到期的> 任务
137 void tick()
138 {
139 if(!head)
140 {
141 return;
142 }
143 printf("timer tick\n");
144 time_t cur = time(NULL); //获得系统当前的时间
145 util_timer* tmp = head;
146 //从头结点开始依次处理每个定时器,直到遇到一个尚未到期的定时器,这就是定时器
的核心逻辑
147 while(tmp)
148 {
149 //比较定时器的超时值和系统当前时间
150 if(cur<tmp->expire)
151 {
152 break;
153 }
154
155 //调用定时器的回调函数,以执行定时任务
156 tmp->cb_func(tmp->user_data);
157
158 //执行完定时器中的定时任务后,将它从链表中删除
159 head = tmp->next;
160 if(head)
161 {
162 head->prev = NULL;
163 }
164 delete tmp;
165 tmp = head;
166 }
167 }
168 private:
169 //私有重载定时器添加函数,添加到结点lst_head之后的链表中
170 void add_timer(util_timer* timer, util_timer* lst_head)
171 {
172 util_timer* prev = lst_head;
173 util_timer* tmp = prev->next;
174 //遍历lst_head节点之后的部分链表,直到找到一个超时时间大于目标定时器的超时时
间的结点,并将目标定时器插入该结点之前
175 while(tmp)
176 {
177 if(timer->expire < tmp->expire)
178 {
179 prev->next = timer;
180 timer->next = tmp;
181 tmp->prev = timer;
182 timer->prev = prev;
183 break;
184 }
185 prev = tmp;
186 tmp = tmp->next;
187 }
188 //如果遍历完lst_head结点之后的部分链表,仍未找到超时时间大于目标定时器时间的
结点,则将目标定时器插入链表尾部,并把它设置为新的尾结点
189 if(!tmp)
190 {
191 prev->next = timer;
192 timer->prev = prev;
193 timer->next = NULL;
194 tail = timer;
195 }
196 }
197 private:
198 util_timer* head;
199 util_timer* tail;
200 };
201
202 #endif
【文章福利】需要C/C++ Linux服务器架构师学习资料加群812855908(资料包括C/C++,Linux,golang技术,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK,ffmpeg等)

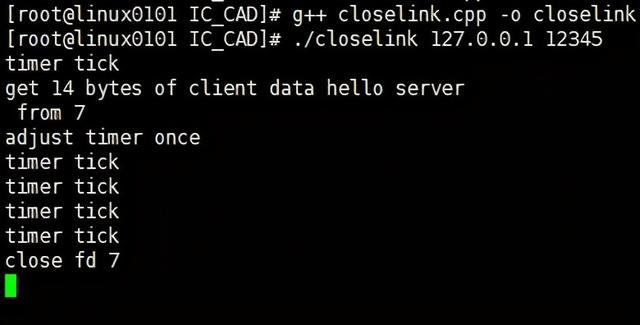
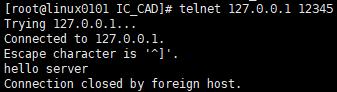
closelink.cpp
1 #include <sys/types.h>
2 #include <sys/socket.h>
3 #include <netinet/in.h>
4 #include <arpa/inet.h>
5 #include <assert.h>
6 #include <stdio.h>
7 #include <signal.h>
8 #include <unistd.h>
9 #include <errno.h>
10 #include <string.h>
11 #include <fcntl.h>
12 #include <stdlib.h>
13 #include <sys/epoll.h>
14 #include <pthread.h>
15 #include "timelink.h"
16
17 #define FD_LIMIT 65535
18 #define MAX_EVENT_NUMBER 1024
19 #define TIMESLOT 5
20 static int pipefd[2];
21 static sort_timer_lst timer_lst;
22 static int epollfd = 0;
23
24 int setnonblocking(int fd)
25 {
26 int old_option = fcntl(fd,F_GETFL);
27 int new_option = old_option | O_NONBLOCK;
28 fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,new_option);
29 return old_option;
30 }
31 void addfd(int epollfd, int fd)
32 {
33 epoll_event event;
34 event.data.fd = fd;
35 event.events = EPOLLIN|EPOLLET;
36 epoll_ctl(epollfd,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,fd,&event);
37 setnonblocking(fd);
38 }
39 void sig_handler(int sig)
40 {
41 int save_errno = errno;
42 int msg = sig;
43 send(pipefd[1],(char*)&msg,1,0);
44 errno = save_errno;
45 }
46 void addsig(int sig)
47 {
48 struct sigaction sa;
49 memset(&sa,'\0',sizeof(sa));
50 sa.sa_handler = sig_handler;
51 sa.sa_flags |= SA_RESTART;
52 sigfillset(&sa.sa_mask);
53 assert(sigaction(sig,&sa,NULL)!=-1);
54 }
55 //定时处理任务,实际上就是调用tick函数
56 void timer_handler()
57 {
58 timer_lst.tick();
59 //因为一次alarm调用只会引起一次SIGALRM信号,需要重新定义,以不断触发SIGALRM信号
60 alarm(TIMESLOT);
61 }
62 //定时器回调函数,它删除非活动连接socket上的注册事件,并关闭之
63 void cb_func(client_data* user_data)
64 {
65 assert(user_data);
66 epoll_ctl(epollfd,EPOLL_CTL_DEL,user_data->sockfd,0);
67 close(user_data->sockfd);
68 printf("close fd %d\n",user_data->sockfd);
69 }
70 int main(int argc, char* argv[])
71 {
72 if( argc <= 2)
73 {
74 printf("usage: %s ip_address port_number\n",basename(argv[0]));
75 return 1;
76 }
77 const char* ip = argv[1];
78 int port = atoi(argv[2]);
79 int ret = 0;
80 struct sockaddr_in address;
81 bzero(&address,sizeof(address));
82 address.sin_family = AF_INET;
83 inet_pton(AF_INET, ip, &address.sin_addr);
84 address.sin_port = htons(port);
85 int listenfd = socket(PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
86 assert(listenfd>=0);
87 ret = bind(listenfd,(struct sockaddr*)&address,sizeof(address));
88 assert(ret!=-1);
89 ret = listen(listenfd,5);
90 assert(ret!=-1);
91 epoll_event events[MAX_EVENT_NUMBER];
92 int epollfd = epoll_create(5);
93 assert(epollfd!=-1);
94 addfd(epollfd,listenfd);
95 ret = socketpair(PF_UNIX,SOCK_STREAM,0,pipefd);
96 assert(ret!=-1);
97 setnonblocking(pipefd[1]);
98 addfd(epollfd,pipefd[0]);
99
100 //设置信号处理函数
101 addsig(SIGALRM);
102 addsig(SIGTERM);
103 bool stop_server = false;
104
105 client_data* users = new client_data[FD_LIMIT];
106 bool timeout = false;
107 alarm(TIMESLOT); //定时
108
109 while(!stop_server)
110 {
111 int number = epoll_wait(epollfd,events,MAX_EVENT_NUMBER,-1);
112 if((number<0)&&(errno!=EINTR))
113 {
114 printf("epoll failure\n");
115 break;
116 }
117 for(int i = 0; i < number; i++)
118 {
119 int sockfd = events[i].data.fd;
120 if(sockfd==listenfd)
121 {
122 //处理新到的客户连接
123 struct sockaddr_in client_address;
124 socklen_t client_addrlength = sizeof(client_address);
125 int connfd = accept(listenfd,(struct sockaddr*)&client_addre ss,&client_addrlength);
126 addfd(epollfd,connfd);
127 users[connfd].address = client_address;
128 users[connfd].sockfd = connfd;
129 //创建定时器,设置其回调函数与超时时间,然后绑定定时器与用户数据,最后将定时器添加到链表timer_lst中
130 util_timer* timer = new util_timer;
131 timer->user_data = &users[connfd];
132 timer->cb_func = cb_func;
133 time_t cur = time(NULL);
134 timer->expire = cur + 3*TIMESLOT;
135 users[connfd].timer = timer;
136 timer_lst.add_timer(timer);
137 }else if((sockfd==pipefd[0])&&(events[i].events & EPOLLIN)){
138 //处理信号
139 int sig;
140 char signals[1024];
141 ret = recv(pipefd[0],signals,sizeof(signals),0);
142 if(ret==-1)
143 {
144 //处理错误
145 continue;
146 }else if(ret == 0)
147 {
148 continue;
149 }else{
150 for(int i = 0; i < ret; ++i)
151 {
152 switch(signals[i])
153 {
154 case SIGALRM:
155 //用timeout标记有定时任务需> 要处理
156 {timeout = true; break;}
157 case SIGTERM:
158 {stop_server = true;}
159 }
160 }
161 }
162 }else if(events[i].events & EPOLLIN)
163 {
164 //处理客户连接上接收到的数据
165 memset(users[sockfd].buf, '\0', BUFFER_SIZE);
166 ret = recv(sockfd,users[sockfd].buf,BUFFER_SIZE-1,0);
167
168 util_timer* timer = users[sockfd].timer;
169 if(ret <0)
170 { //如果发生读错误,则关闭连接,并移除其对应的定时器
171 if(errno!=EAGAIN)
172 {
173 cb_func(&users[sockfd]);
174 if(timer)
175 {
176 timer_lst.del_timer(timer);
177 }
178 }
179 }else if(ret == 0)
180 { //如果对方关闭连接,则服务器也关闭连接,并移除对应的
定时器
181 cb_func(&users[sockfd]);
182 if(timer)
183 {
184 timer_lst.del_timer(timer);
185 }
186 }else{ //如果某个客户连接上有数据,则要调整该连接对应的定时> 器,以延迟该连接被关闭的时间
187 printf("get %d bytes of client data %s from %d\n",re t,users[sockfd].buf,sockfd);
188 if(timer)
189 {
190 time_t cur = time(NULL);
191 timer->expire = cur + 3*TIMESLOT;
192 printf("adjust timer once\n");
193 timer_lst.adjust_timer(timer);
194 }
195 }
196 }else{
197 //others
198 }
199 }
200 //最后处理定时事件,因为I/O事件有更高优先级,这样会导致定时任务不能按照预期> 时间执行
201 if(timeout)
202 {
203 timer_handler();
204 timeout = false;
205 }
206 }
207 close(listenfd);
208 close(pipefd[1]);
209 close(pipefd[0]);
210 delete[] users;
211 return 0;
212 }
I/O复用系统调用的超时参数
Linux下的3组I/O复用系统调用都带有超时参数,因此它们不仅能统一处理信号和I/O事件,也能统一处理定时事件。但是由于I/O复用系统调用可能在超时时间到期之前就返回(有I/O事件发生),所以如果要利用它们来定时,就需要不断更新定时参数以反映剩余的时间。
#define TIMEOUT 5000
int timeout = TIMEOUT;
time_t start = time(NULL);
time_t end = time(NULL);
while(1)
{
printf("the timeout is now %d mil-seconds\n",timeout);
start = time(NULL);
int number = epoll_wait(epollfd,events,MAX_EVENT_NUMBER,timeout);
if((number<0)&&(errno!=EINTR))
{
printf("epoll failure\n");
break;
}
//如果epoll_wait成功返回0,则说明超时时间到,此时便可处理定时任务,并重置定时时间
if(number==0)
{
timeout = TIMEOUT;
continue;
}
end = time(NULL);
//如果epoll_wait的返回值大于0,则本次epoll_wait调用持续的时间是(end-start)*1000ms,我们需要将定时时间timeout减去这段时间,以获得下次epoll_wait调用的超时参数
timeout -= (end-start)*1000;
//重新计算后timeout有可能等于0,说明本次epoll_wait调用返回时,不仅有文件描述符就绪,而且其超时时间也刚好到达,此时我们也要处理定时任务,并重置定时时间
if(timeout <= 0)
{
timeout = TIMEOUT;
}
//handle connections
}
高性能定时器
时间轮
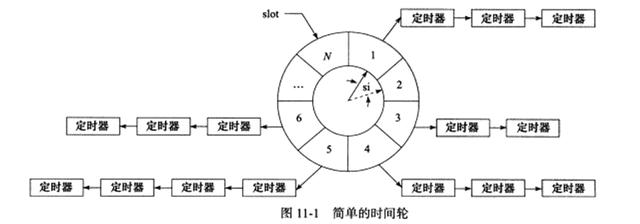
在时间轮内,(实线)指针指向轮子上的一个槽(slot),它以恒定的速度顺时针转动,每转动一步就指向下一个槽(虚线指针指向的槽),每次转动称为一个滴答(tick)。一个滴答的时间称为时间轮的槽间隔si(slot interval),它实际上就是心搏时间。该时间轮共有N个槽,因此它运转一周的时间是Nsi。每个槽指向一条定时器链表,每条链表上的定时器具有相同的特征:它们的定时时间相差Nsi的整数倍。时间轮正是利用这个关系将定时器散列到不同的链表中。假如现在指针指向槽cs,我们要添加一个定时时间为ti的定时器,则该定时器将被插入槽ts(timer slot)对应的链表中:ts=(cs+(ti/si))%N
基于排序链表的定时器使用唯一的一条链表来管理所有定时器,所以插入操作的效率随着定时器数目的增多而降低。而时间轮私用哈希表的思想,将定时器散列到不同的链表上。这样每条链表上的定时器数目都将明显少于原来的排序链表上的定时器数目,插入操作的效率基本不受定时器数目的影响。对于时间轮而言,添加一个定时器的时间复杂度是O(1),删除一个定时器的时间复杂度也是O(1),指向一个定时器的时间复杂度是O(n)。但实际上执行一个定时器任务的效率要比O(n)好得多,因为时间轮将所有的定时器散列到了不同的链表上。时间轮的槽越多,等价于散列表的入口越多,从而每条链表上的定时器数量越少。
timeround.h
1 #ifndef TIME_WHEEL_TIMER
2 #define TIME_WHEEL_TIMER
3 #include <time.h>
4 #include <netinet/in.h>
5 #include <stdio.h>
6 #define BUFFER_SIZE 64
7 class tw_timer;
8 struct client_data
9 {
10 sockaddr_in address;
11 int sockfd;
12 char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
13 tw_timer* timer;
14 };
15 class tw_timer
16 {
17 pubilc:
18 tw_timer(int rot, int ts):rotation(rot),time_slot(ts),next(NULL),prev(NULL){}
19 int rotation; //记录定时器在时间轮转多少圈后生效
20 int time_slot; //记录定时器属于时间轮上哪个槽
21 void (*cb_func)(client_data*); //定时器回调函数
22 client_data* user_data; //客户数据
23 tw_timer* next; //指向下一个定时器
24 tw_timer* prev; //指向前一个定时器
25 };
26
27 class time_wheel
28 {
29 public:
30 time_wheel():cur_slot(0)
31 {
32 for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
33 {
34 slots[i] = NULL;
35 }
36 }
37 ~time_wheel()
38 {
39 for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
40 {
41 tw_timer* tmp = slots[i];
42 while(tmp)
43 {
44 slots[i] = tmp->next;
45 delete tmp;
46 tmp = slots[i];
47 }
48 }
49 }
50
51 //根据定时值timeout创建一个定时器,并把它插入何时的槽中
52 tw_timer* add_timer(int timeout)
53 {
54 if(timeout < 0)
55 {
56 return NULL;
57 }
58 int ticks = 0;
59 //下面根据待插入定时器的超时值计算它将在时间轮转动多少个滴答后被触发
60 //并将该滴答数存储于变量ticks中。如果待插入定时器的超时值小于时间轮
61 //的槽间隔SI,则将ticks向上折合为1,否则就将ticks向下折合为timeout/SI
62 if(timeout < SI)
63 {
64 ticks = 1;
65 }else{
66 ticks = timeout / SI;
67 }
68 //计算待插入的定时器在时间轮转动多少圈后被触发
69 int rotation = ticks/N;
70 //计算待插入的定时器应该被插入哪个槽中
71 int ts = (cur_slot+(ticks%N))%N;
72 //创建新的定时器,它在时间轮转动rotation圈之后被触发,且位于第ts个槽
73 tw_timer* timer = new tw_timer(rotation,ts);
74 //如果第ts个槽中尚无任何定时器,则把新建的定时器插入其中,并将该定时器设置为该槽的头
结点
75 if(!slots[ts])
76 {
77 printf("add timer, rotation is %d, ts is %d, cur_slot is %d\n",rotation,ts,c ur_slot);
78 slots[ts] = timer;
79 }else{
80 //否则将定时器插入第ts个槽中
81 timer->next = slots[ts];
82 slots[ts]->prev = timer;
83 slots[ts] = timer;
84 }
85 return timer;
86 }
87
88 //删除目标定时器timer
89 void del_timer(tw_timer* timer)
90 {
91 if(!timer)
92 {
93 return;
94 }
95 int ts = timer->time_slot;
96 //slots[ts]是目标定时器所在槽的头结点
97 if(timer==slots[ts])
98 {
99 slots[ts] = slots[ts]->next;
100 if(slots[ts])
101 {
102 slots[ts]->prev = NULL;
103 }
104 delete timer;
105 }else{
106 timer->prev->next = timer->next;
107 if(timer->next)
108 {
109 timer->next->prev = timer->prev;
110 }
111 delete timer;
112 }
113 }
114
115 //SI时间到后,调用该函数,时间轮向前滚动一个槽的间隔
116 void tick()
117 {
118 tw_timer* tmp = slots[cur_slot]; //取得时间轮上当前槽的头结点
119 printf("current slot is %d\n",cur_slot);
120 while(tmp)
121 {
122 printf("tick the timer once\n");
123 //如果定时器的rotation值大于0,则它在这一轮不起作用
124 if(tmp->rotation>0)
125 {
126 tmp->rotation--;
127 tmp = tmp->next;
128 }else{
129 //定时器已经到期,于是执行定时任务,然后删除该定时器
130 tmp->cb_func(tmp->user_data);
131 if(tmp==slots[cur_slot])
132 {
133 printf("delete header in cur_slot\n");
134 slots[cur_slot] = tmp->next;
135 delete tmp;
136 if(slots[cur_slot])
137 {
138 slots[cur_slot]->prev = NULL;
139 }
140 tmp = slots[cur_slot];
141 }else{
142 tmp->prev->next = tmp->next;
143 if(tmp->next)
144 {
145 tmp->next->prev = tmp->prev;
146 }
147 tw_timer* tmp2 = tmp->next;
148 delete tmp;
149 tmp = tmp2;
150 }
151
152 }
153 }
154 //更新时间轮的当前槽
155 cur_slot = ++cur_slot % N;
156 }
157 private:
158 static const int N = 60; //时间轮上槽的数目
159 static const int SI = 1; //每1s时间轮转动一次,即槽间隔为1s
160 tw_timer* slots[N]; //时间轮的槽,其中每个元素指向一个定时器链表,链表无序
161 int cur_slot; //时间轮的当前槽
162
163 };
164
165 #endif
时间堆
前面讨论的定时方案都是以固定的频率调用心搏tick,并在其中依次检测到期的定时器,然后执行到期定时器上的回调函数。设计定时器的另外一种思路是:将所有定时器中超时时间最小的一个定时器的超时值作为心搏间隔。这样,一旦心搏tick被调用,超时时间最小的定时器必然到期,我们就可以在tick函数中处理该定时器。然后,再次从剩余的定时器中找出超时时间最小的一个,并将这段最小时间设置为下一次心搏间隔。如此反复,就实现了较为精确的定时。
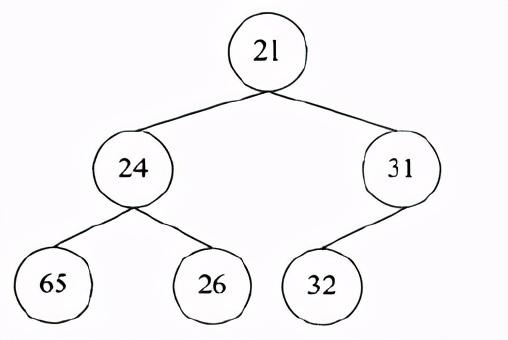
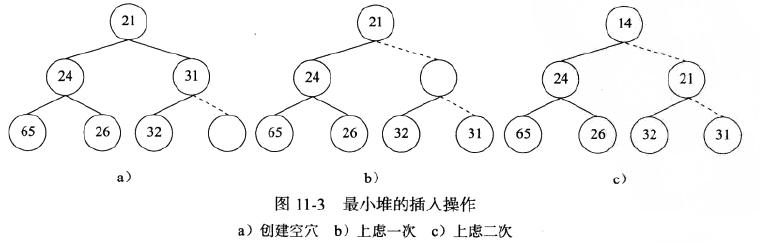
最小堆是指每个节点的值都小于或等于其子节点的值的完全二叉树。树的基本操作是插入节点和删除节点。为了将一个元素X插入最小堆,我们可以在树的下一个空闲位置创建一个空穴。如果X可以放在空穴中而不破坏堆序,则插入完成。否则就执行上虑操作,即交换空穴和它的父节点上的元素。不断执行上述过程,直到X可以被放入空穴,则插入操作完成。
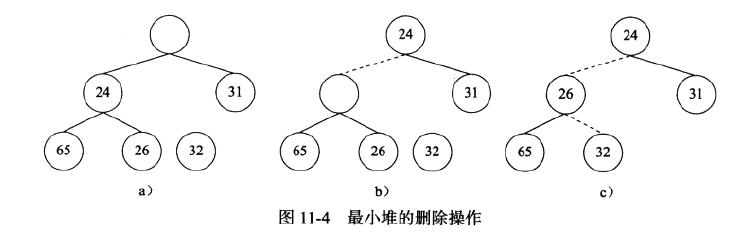
最小堆的删除操作指的是删除其根节点上的元素,并且不被坏堆序性质。执行删除操作时,我们需要先在根节点处创建一个空穴。由于堆现在少了一个元素,因此我们可以把堆的最后一个元素X移动到该堆的某个地方。如果X可以被放入空穴,则删除操作完成。否则就执行下虑操作,即交换空穴和它的两个儿子节点中的较小者。不断进行上述过程,直到X可以被放入空穴,则删除操作完成。
由于最小堆是一种完全二叉树,所以可以用数组来组织其中的元素。比如第一幅图所示的最小堆可以用下图表示。对于数组中的任意一个位置i上的元素,其左儿子节点在位置2i+1上,其右儿子节点在位置2i+2上,其父节点则在位置[(i-1)/2] (i>0)上。与用链表来表示堆相比,用数组表示堆不仅节省空间,而且更容易实现堆的插入、删除等操作。

假设我们已经有一个包含N个元素的数组,现在要把它初始化为一个最小堆。那么最简单的方法是:初始化一个空堆,然后将数组中的每个元素插入该堆中。不过这样做效率偏低。实际上,我们只需要对数组中的第[(N-1)/2] ~ 0个元素执行下虑操作,即可保证该数组构成一个最小堆。这是因为对包含N个元素的完全二叉树而言,它具有[(N-1)/2]个非叶子节点,这些非叶子节点正是该完全二叉树的第0 ~ [(N-1)/2]个节点。我们只要确保这些非叶子节点构成的子树都具有堆序性质,整个树就具有堆序性质。
timestack.h
1 #ifndef MIN_HEAP
2 #define MIN_HEAP
3 #include <iostream>
4 #include <netinet/in.h>
5 #include <time.h>
6 using std::exception;
7 #define BUFFER_SIZE 64
8
9 class heap_timer;
10 struct client_data
11 {
12 sockaddr_in address;
13 int sockfd;
14 char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
15 heap_timer* timer;
16 };
17 class heap_timer
18 {
19 public:
20 heap_timer(int delay) { expire = time(NULL) + delay; }
21 time_t expire; //定时器生效的绝对时间
22 void (*cb_func)(client_data*); //定时器的回调函数
23 client_data* user_data; //用户数据
24 };
25
26 class time_heap
27 {
28 public:
29 time_heap(int cap) throw(std::exception):capacity(cap),cur_size(0)
30 {
31 array = new heap_timer* [capacity];
32 if(!array)
33 {
34 throw std::exception();
35 }
36 for(int i = 0; i < capacity; ++i)
37 {
38 array[i] = NULL;
39 }
40 }
41 time_heap(heap_timer** init_array, int size, int capacity) throw(std::exception):
42 capacity(capacity),cur_size(size)
43 {
44 if(capacity<size)
45 {
46 throw std::exception();
47 }
48 array = new heap_timer* [capacity];
49 if(!array)
50 {
51 throw std::exception();
52 }
53 for(int i = 0; i < capacity; ++i)
54 {
55 array[i] = NULL;
56 }
57 if(size!=0)
58 {
59 for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
60 {
61 array[i] = init_array[i];
62 }
63 for(int i = (cur_size-1)/2; i >=0; --i)
64 { //对数组中的第[(cur_size-1)/2]~0个元素执行下虑操作
65 percolate_down(i);
66 }
67 }
68 }
69 ~time_heap()
70 {
71 for(int i =0; i < cur_size; ++i)
72 {
73 delete array[i];
74 }
75 delete [] array;
76 }
77
78 //添加目标定时器timer
79 void add_timer(heap_timer* timer) throw(std::exception)
80 {
81 if(!timer)
82 {
83 return;
84 }
85 if(cur_size>=capacity)
86 {
87 resize();
88 }
89 //新插入一个元素,当前堆大小加1,hole是新建空穴的位置
90 int hole = cur_size++;
91 int parent = 0;
92 //对从空穴到梗节点的路径上的所有节点执行上虑操作
93 for(;hole>0;hole=parent)
94 {
95 parent = (hole-1)/2;
96 if(array[parent]->expire <= timer->expire)
97 {
98 break;
99 }
100 array[hole] = array[parent];
101 }
102 array[hole] = timer;
103 }
104
105 //删除目标定时器timer
106 void del_timer(heap_timer* timer)
107 {
108 if(!timer)
109 {
110 return;
111 }
112 //仅将目标定时器的回调函数设置为空,即所谓的延迟销毁
113 //这节省真正删除该定时器造成的开销,但容易使堆数组膨胀
114 timer->cb_func = NULL;
115 }
116
117 //获得堆顶部的定时器
118 heap_timer* top() const
119 {
120 if(empty())
121 {
122 return NULL;
123 }
124 return array[0];
125 }
126
127 //删除堆顶部的定时器
128 void pop_timer()
129 {
130 if(empty())
131 {
132 return;
133 }
134 if(array[0])
135 {
136 delete array[0];
137 //将原来的堆顶元素替换为堆数组中最后一个元素
138 array[0] = array[--cur_size];
139 percolate_down(0); //对新的堆顶元素执行下虑操作
140 }
141 }
142
143 //心搏函数,处理一批到期的定时器
144 void tick()
145 {
146 heap_timer* tmp = array[0];
147 time_t cur = time(NULL);
148 while(!empty())
149 {
150 if(!tmp)
151 {
152 break;
153 }
154 //如果堆顶定时器没有到期,则退出循环
155 if(tmp->expire > cur)
156 {
157 break;
158 }
159 //否则就执行堆顶定时器中的任务
160 if(array[0]->cb_func)
161 {
162 array[0]->cb_func(array[0]->user_data);
163 }
164 //将堆顶元素删除,同时生成新的堆顶定时器
165 pop_timer();
166 tmp = array[0];
167 }
168 }
169
170 //判空函数
171 bool empty() const { return cur_size == 0; }
172 private:
173 //最小堆的下虑操作,它确保数组中以第hole个节点作为根的子树拥有最小堆性质
174 void percolate_down(int hole)
175 {
176 heap_timer* temp = array[hole];
177 int child = 0;
178 //hole当前节点 hole*2+1左子节点
179 for(;(hole*2+1)<=(cur_size-1);hole=child)
180 {
181 child = hole*2+1;
182 if((child<(cur_size-1))&&(array[child+1]->expire < array[child]->expire))
183 {
184 ++child; //找到子节点超时值小的
185 }
186 if(array[child]->expire < temp->expire)
187 {
188 array[hole] = array[child];
189 }else{
190 break;
191 }
192 }
193 array[hole] = temp;
194 }
195
196 //将堆数组容量扩大1倍
197 void resize() throw(std::exception)
198 {
199 heap_timer** temp = new heap_timer* [2*capacity];
200 if(!temp)
201 {
202 throw std::exception();
203 }
204 for(int i = 0; i < 2*capacity; ++i)
205 {
206 temp[i] = NULL;
207 }
208 capacity = 2 * capacity;
209 for(int i = 0; i < cur_size; ++i)
210 {
211 temp[i] = array[i];
212 }
213 delete [] array;
214 array = temp;
215 }
216
217 heap_timer** array; //堆数组
218 int capacity; //堆数组的容量
219 int cur_size; //堆数组当前包含元素的个数
220 };
221
222 #endif
对于时间堆而言,添加一个定时器的时间复杂度是O(lgn),删除一个定时器的时间复杂度是O(1),执行一个定时器的时间复杂度是O(1)。


