一、简介
1. 课程背景
分布式 系统的根基在于网络编程,而 Netty 是 Java 领域网络编程的王者。
2. 课程内容
第一部分 NIO 编程,三大组件
第二部分 netty 入门学习,EventLoop、Channel、Future、Pipeline、 Handler 、 byte Buf
第三部分 Netty 进阶学习,粘包半包的解决方法、协议的设计、 序列化 知识
第四部分 Netty 常见参数的学习及优化
第五部分 源码
二、NIO 基础
non Blocking IO 非阻塞 IO
1. 三大组件
1.1 Channel & Buffer
channel 有一点类似于 stream,它就是读写数据的双向通道,可以从 channel 将数据读入 buffer,也可以将 buffer 的数据写入 channel,而之前的 stream 要么是写入,要么是输出。
常见的 Channel 有:
File Channel
DatagramChannel
socket Channel
ServerSocketChannel
buffer 则用来缓冲读写数据,常见的 buffer 有:
ByteBuffer
MappedByteBuffer
DirectByteBuffer
HeapByteBuffer
short /Int/Long/Float/Double/Char Buffer
1.2 Selector
使用多线程技术
为每个连接分别开辟一个 线程 ,分别去处理对应的 socket 连接
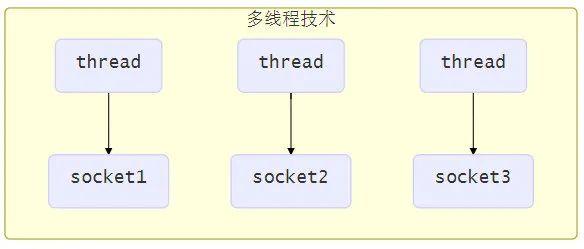
:exclamation: 多线程缺点
内存占用高
线程上下文切换成本高
只适合连接数较少的场景
使用 线程池 技术
使用线程池,让线程池中的线程去处理连接
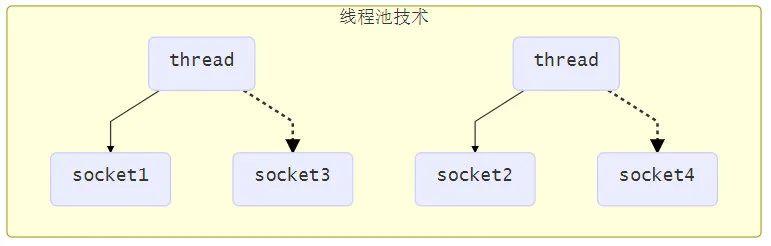
这种方式存在以下几个问题:
阻塞模式下,线程仅能处理一个连接
仅适合短连接场景
使用 Selector
selector 的作用就是配合一个线程来管理多个 channel( file Channel 因为是阻塞式的,所以无法使用 selector),获取这些 channel 上发生的事件,这些 channel 工作在非阻塞模式下,当一个 channel 中没有执行任务时,可以去执行其他 channel 中的任务。适合连接数多,但流量较少的场景。
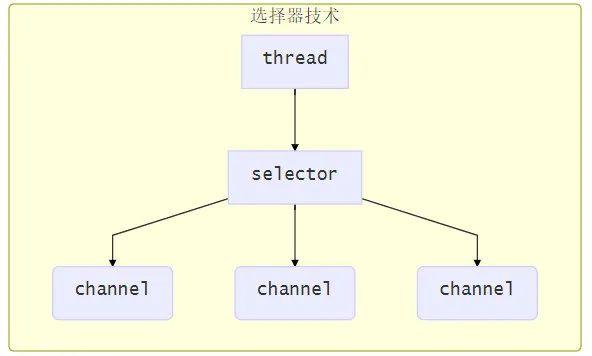
若事件未就绪,调用 selector 的 select 方法会阻塞线程,直到 channel 发生了就绪事件。这些事件就绪后,select 方法就会返回这些事件交给 thread 来处理。
2.ByteBuffer
使用案例
有一普通文本文件 data.txt 内容为
1234567890abc
使用 FileChannel 来读取文件内容
@Slf4j
public class Test ByteBuffer {
public static void main (String[] args) {
// FileChannel
// 1.输入输出流 2.RandomAccessFile
try {
FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel;
// 准备缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
// 从 Channel 中读取数据,向 Buffer 写入
int len;
while ((len = fileChannel.read(buf)) != -1) {
log .info("读取到的字节:{}", len );
buf.flip; // 切换至读模式
log.debug("输出内容为:{}", new String(buf.array, 0, len));
// while (buf.hasRemaining) { // 是否还剩余数据
// byte b = buf.get;
// log.debug("输出内容为:{}", (char) b);
// }
// 切换为写模式
buf.clear;
}
} catch (IO Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace;
}
}
}
2.1 ByteBuffer 使用步骤
向 buffer 写入数据,e.g. 调用
channel.read(buf)调用
flip切换至读模式向 buffer 读取数据,e.g. 调用
buf.get调用
clear或compact切换至写模式重复 1~4 步骤
2.2 ByteBuffer 结构
核心属性
字节缓冲区的父类 Buffer 中有几个核心属性,如下:
// Invariants: mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
private int mark = -1;
private int position = 0;
private int limit;
private int capacity;
capacity:缓冲区的容量。通过构造函数赋予,一旦设置,无法更改。limit:缓冲区的界限。位于 limit 后的数据不可读写。缓冲的限制不能为负,并且不能大于其容量。position:下一个读写位置的索引(类似 PC)。缓冲区的位置不能为负,并且不能大于 limit。mark:记录当前 position 的值。position 被改变后,可以通过调用reset方法恢复到 mark 的位置。
核心方法:
put 方法
put 方法可以将一个数据放入缓冲区
进行该操作后,position 的值会 +1,指向下一个可以放入的位置。capacity = limit。
flip 方法
flip 方法会切换对缓冲区的操作模式,由写 -> 读 / 读 -> 写
进行该操作后
如果是 写模式 -> 读模式,position = 0,limit 指向最后一个元素的下一个位置,capacity 不变
如果是读 -> 写,则恢复为 put 方法中的值
get 方法
get方法会读取缓冲区中的一个值进行该操作后,position 会 +1,如果超过了 limit 则会抛出异常
注意:
get(i)方法不会改变 position 的值
rewind 方法
该方法只能在读写模式下使用
rewind方法后,会恢复 position、limit 和 capacity 的值,变为进行 get 前的值
clean 方法
clean 方法会将缓冲区中的各个属性恢复为最初的状态,position = 0,capacity = limit
此时,缓冲区的数据依然存在,处于“被遗忘”状态,下次进行写操作时会覆盖这些数据
mark 和 reset 方法
mark 方法会将 position 的值保存到 mark 属性中
reset 方法会将 position 的值改为 mark 中保存的值
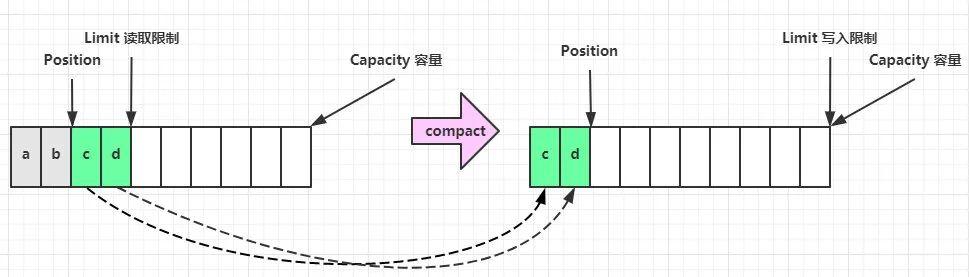
compact 方法
此方法为 ByteBuffer 的方法,而不是 Buffer 的方法
compact 会把未读完的数据向前压缩,然后切换到写模式
数据前移后,原位置的值并未清零,写时会覆盖之前的值
2.2 ByteBuffer 结构
ByteBuffer 有以下重要属性
capacity
position
limit
刚开始
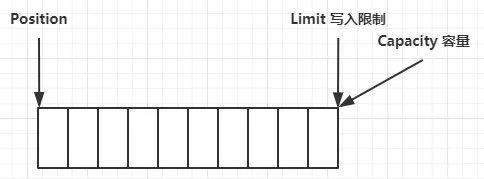
写模式下,position 是写入位置,limit 等于容量,下图表示写入了 4 个字节后的状态。
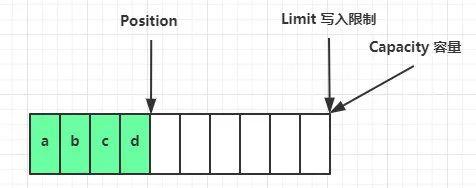
flip 动作发生后,position 切换为读取位置,limit 切换为读取限制。
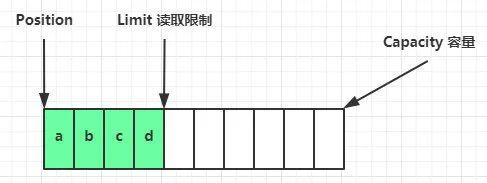
读取 4 个 byte 后,状态:
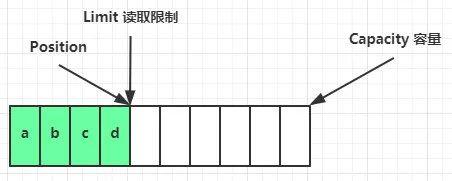
clear 动作发生后,状态变为一开始。
compact 方法,是把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式。
💡 调试工具类
导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.51.Final</version>
</dependency>
public class ByteBufferUtil {
private static final char BYTE2CHAR = new char[256];
private static final char HEXDUMP_TABLE = new char[256 * 4];
private static final String HEXPADDING = new String[16];
private static final String HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES = new String[65536 >>> 4];
private static final String BYTE2HEX = new String[256];
private static final String BYTE padding = new String[16];
static {
final char DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
HEXDUMP_TABLE[i << 1] = DIGITS[i >>> 4 & 0x0F];
HEXDUMP_TABLE[(i << 1) + 1] = DIGITS[i & 0x0F];
}
int i;
// Generate the lookup table for hex dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < HEXPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = HEXPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding * 3);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(" ");
}
HEXPADDING[i] = buf.toString;
}
// Generate the lookup table for the start-offset header in each row (up to 64KiB).
for (i = 0; i < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length; i++) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(12);
buf.append(NEWLINE);
buf.append(Long.toHexString(i << 4 & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
buf.setCharAt(buf.length - 9, '|');
buf.append('|');
HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[i] = buf.toString;
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-hex-dump conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2HEX.length; i++) {
BYTE2HEX[i] = ' ' + StringUtil.byteToHexStringPadded(i);
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < BYTEPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = BYTEPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(' ');
}
BYTEPADDING[i] = buf.toString;
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-char conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2CHAR.length; i++) {
if (i <= 0x1f || i >= 0x7f) {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = '.';
} else {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = (char) i;
}
}
}
/**
* 打印所有内容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugAll (ByteBuffer buffer) {
int oldlimit = buffer.limit;
buffer.limit(buffer.capacity);
StringBuilder origin = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(origin, buffer, 0, buffer.capacity);
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]n", buffer.position, oldlimit);
System.out.println(origin);
buffer.limit(oldlimit);
}
/**
* 打印可读取内容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugRead (ByteBuffer buffer) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(builder, buffer, buffer.position, buffer.limit - buffer.position);
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- read -----------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]n", buffer.position, buffer.limit);
System.out.println(builder);
}
private static void appendPrettyHexDump (StringBuilder dump, ByteBuffer buf, int offset, int length) {
if (isOutOfBounds(offset, length, buf.capacity)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"expected: " + "0 <= offset(" + offset + ") <= offset + length(" + length
+ ") <= " + "buf.capacity(" + buf.capacity + ')');
}
if (length == 0) {
return;
}
dump.append(
" +-------------------------------------------------+" +
NEWLINE + " | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |" +
NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
final int startIndex = offset;
final int fullRows = length >>> 4;
final int remainder = length & 0xF;
// Dump the rows which have 16 bytes.
for (int row = 0; row < fullRows; row++) {
int rowStartIndex = (row << 4) + startIndex;
// Per-row prefix.
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, row, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + 16;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(" |");
// ASCII dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append('|');
}
// Dump the last row which has less than 16 bytes.
if (remainder != 0) {
int rowStartIndex = (fullRows << 4) + startIndex;
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, fullRows, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + remainder;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(HEXPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append(" |");
// Ascii dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(BYTEPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append('|');
}
dump.append(NEWLINE +
"+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
}
private static void appendHexDumpRowPrefix (StringBuilder dump, int row, int rowStartIndex) {
if (row < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length) {
dump.append(HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[row]);
} else {
dump.append(NEWLINE);
dump.append(Long.toHexString(rowStartIndex & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
dump.setCharAt(dump.length - 9, '|');
dump.append('|');
}
}
public static short getUnsignedByte (ByteBuffer buffer, int index) {
return (short) (buffer.get(index) & 0xFF);
}
}
测试:
public static void main (String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
// 向 buffer 写入一个数据
buffer.put((byte) 97);
debugAll(buffer);
// 获取数据
buffer.flip;
debugAll(buffer);
System.out.println((char) buffer.get);
debugAll(buffer);
// 使用 compact 切换模式
buffer.compact;
debugAll(buffer);
// 再次写入
buffer.put((byte) 98);
buffer.put((byte) 99);
debugAll(buffer);
}
结果:
10:01:36.720 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLoggerFactory - Using SLF4J as the default logging framework
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [1], limit: [16]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |a...............|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [1]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |a...............|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
a
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [1], limit: [1]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |a...............|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [16]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |a...............|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [2], limit: [16]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 62 63 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |bc..............|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
2.3 ByBuffer 常见方法
分配空间 allocate
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
向 buffer 写入数据
调用 channel 的
read方法调用 buffer 的
put方法
int read = channel.read(buf);
// 第二种
buf.put((byte) 97);
从 buffer 读取数据
调用 channel 的
write方法调用 buffer 的
get方法
int writeBytes = channel.write(buf);
byte b = buf.get;
get 方法会让 position 读指针后移,如果想重复读取数据
可以调用
rewind方法将 position 重置为 0.public final Buffer rewind {
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
或者调用
get(int i)获取索引 i 的内容,不会移动读指针。
mark and reset
mark 是在读取时,做一个标记,即使 position 改变,只要调用 reset 就能够回到 mark 的位置
字符串与 ByteBuffer 互转
// 字符串与 ByteBuffer 互转
// 1.还是写模式
byte bytes = "hello".getBytes;
ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
buf2.put(bytes);
debugAll(buf2);
// 2.Charset,切换到读模式
ByteBuffer buf3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
debugAll(buf3);
// 3.wrap 方法,切换到读模式
ByteBuffer buf4 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes);
debugAll(buf4);
System.out.println((char) buf4.get); // h
// ByteBuffer --> String
String buf2Str = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buf3).toString;
System.out.println(buf2Str);
Buffer 的线程安全
Buffer 是非线程安全的。
2.4 Scattering Reads
分散读取,有一个文本文件
onttwothree
使用如下方式读取,可以将数据填充至多个 buffer
// 分散读取
try {
FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("words.txt", "r").getChannel;
ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer buf3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{buf1, buf2, buf3});
buf1.flip;
buf2.flip;
buf3.flip;
debugAll(buf1);
debugAll(buf2);
debugAll(buf3);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace;
}
12:58:55.475 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLoggerFactory - Using SLF4J as the default logging framework
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [3]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 6f 6e 65 |one |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [3]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 74 77 6f |two |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 74 68 72 65 65 |three |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
2.5 Gathering Writes
try {
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("words2.txt", "rw");
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel;
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
channel.position(11);
buf.put(new byte[]{'f', 'o', 'u', 'r'});
buf2.put(new byte[]{'f', 'i', 'v', 'e'});
buf.flip;
buf2.flip;
debugAll(buf);
debugAll(buf2);
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{buf, buf2});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace;
}
13:05:19.694 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLoggerFactory - Using SLF4J as the default logging framework
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [4]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 66 6f 75 72 |four |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [4]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 66 69 76 65 |five |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
2.6 粘包、半包现象
网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 n 进行分隔;但由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有 3 条为:
hello, worldn
I'm zhangsann
How are you?n
变成了下面的两个 ByteBuffer
hello, worldnI'm zhangsannHo
w are you?n
要求编写程序,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的 n 分隔的数据。
public static void main (String[] args) {
// 黏包、半包
ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
source.put("Hello, worldnI'm zhangsannHo".getBytes);
split(source);
source.put("w are you?n".getBytes);
split(source);
}
private static void split (ByteBuffer source) {
// 传进来的参数是写模式,切换到读模式
source.flip;
for (int i = 0; i < source.limit; i++) {
if (source.get(i) == 'n') {
int len = i + 1 - source.position;
// 把这条完整的消息写入到新的 ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(len);
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
target.put(source.get);
}
debugAll(target);
}
}
// 切换到写模式,有些数据被拆分,所以使用 compact
source.compact;
}
13:26:33.581 [main] DEBUG io.netty.util.internal.logging.InternalLoggerFactory - Using SLF4J as the default logging framework
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [13], limit: [13]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 48 65 6c 6c 6f 2c 20 77 6f 72 6c 64 0a |Hello, world. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [13], limit: [13]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 49 27 6d 20 7a 68 61 6e 67 73 61 6e 0a |I'm zhangsan. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [13], limit: [13]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 48 6f 77 20 61 72 65 20 79 6f 75 3f 0a |How are you?. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
3.文件编程
3.1 FileChannel
FileChannel 只能工作在阻塞模式下
获取
不能直接打开 FileChannel,必须通过 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 来获取 FileChannel,它们都有 getChannel 方法。
通过 FileInputStream 获取的 channel 只能读
通过 FileOutputStream 获取的 channel 只能写
通过 RandomAccessFile 是否能读写根据构造 RandomAccessFile 时的读写模式决定。
读取
返回 -1 表示达到了文件的末尾。
int read = channel.read(buf);
写入
ByteBuffer buf = ...;
buf.put(...); // 存入数据
buf.flip; // 切换读模式
while (buf.hasRemaining) {
channel.write(buf);
}
在 while 中调用 channel.write 是因为 write 方法并不能保证一次将 buffer 中的内容全部写入 channel.
关闭
channel 必须关闭,不过调用了 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 的 close 方法会间接地调用 channel 的 close 方法。
位置
long pos = channel.position; // 获取当前位置
long newPos = ...;
channel.position(newPos); // 设置当前位置
设置当前位置时,如果设置为文件的末尾
这时会返回 -1
这时写入,会追加内容,但是注意如果 position 超过了文件末尾,再写入时在新内容和原末尾之间会有空洞(00)。
大小
channel.size; // 获取文件的大小
强制写入
操作系统出于性能的考虑,会将数据缓存,不是立刻写入磁盘。可以调用 force(true) 方法将文件内容和元数据(文件的权限等信息)立刻写入磁盘.
3.2 两个 Channel 传输数据
public static void main (String[] args) {
try (FileChannel from = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel;
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream("to.txt").getChannel;
) {
// 效率高,底层会利用操作系统的零拷贝进行优化
// from.transferTo(0, from.size, to);
long size = from.size;
for (long left = size; left > 0; ) {
left -= from.transferTo((size - left), left, to);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace;
}
}
3.3 Path
jdk7 引入了 Path 和 Paths 类
Path 用来表示文件路径
Paths 是工具类,用来获取 Path 实例
Path source = Paths.get("1.txt");
sout(source.normalize); // 正常化路径
3.4 Files
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Files.exists(path) | 检查文件是否存在 |
| Files.createDirectory(path) |
|
| Files.createDirectories(path) | 创建多及目录 |
| 拷贝文件,如果文件已存在,抛异常 |
| Files.move(source, target, StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE); | 移动文件,StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE 保证文件移动的原子性 |
| Files.delete(target) |
|
遍历目录文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get("E:BaiduNetdiskDownloadNetty网络编程");
// 文件目录总数
AtomicInteger dirCount = new AtomicInteger;
// 文件总数
AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger;
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path> {
@Override
public FileVisitResult preVisitDirectory(Path dir, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-->" + dir);
dirCount.getAndIncrement;
return super.preVisitDirectory(dir, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
System.out.println("file: " + file);
fileCount.getAndIncrement;
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
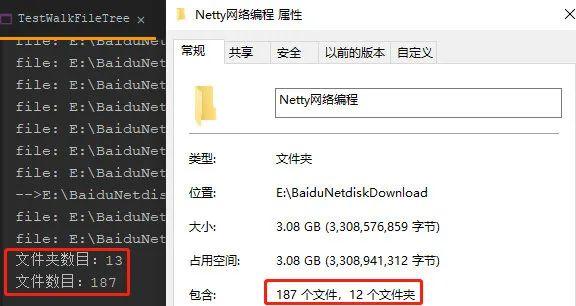
System.out.println("文件夹数目:" + dirCount);
System.out.println("文件数目:" + fileCount);
}
SimpleFileVisitor
运行结果:
统计 .md 文档的数目
Path path = Paths.get("E:BaiduNetdiskDownloadNetty网络编程");
// 统计 .md 文档数目
AtomicInteger mdCnt = new AtomicInteger;
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path> {
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
if (file.toString.endsWith(".md")) { // toFile.toString.
System.out.println(file.toString);
mdCnt.incrementAndGet;
}
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println("md文档数目:" + mdCnt);
删除多级目录
Path path = Paths.get("d:a");
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>{
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException {
Files.delete(file);
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory(Path dir, IOException exc)
throws IOException {
Files.delete(dir);
return super.postVisitDirectory(dir, exc);
}
});
拷贝多级目录
long start = System.currentTimeMillis;
String source = "D:Snipaste-1.16.2-x64";
String target = "D:Snipaste-1.16.2-x64aaa";
Files.walk(Paths.get(source)).forEach(path -> {
try {
String targetName = path.toString.replace(source, target);
// 是目录
if (Files.isDirectory(path)) {
Files.createDirectory(Paths.get(targetName));
}
// 是普通文件
else if (Files.isRegularFile(path)) {
Files.copy(path, Paths.get(targetName));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace;
}
});
long end = System.currentTimeMillis;
System.out.println(end - start);


