Java CheatSheet
基础
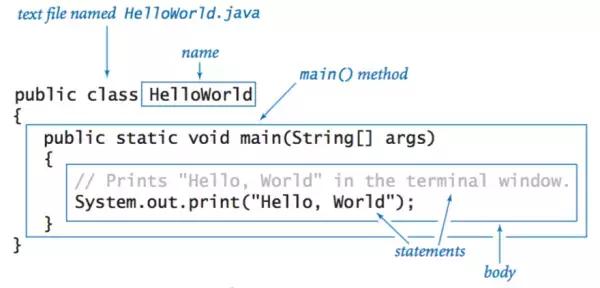
hello, world! :
if-else:

loops:

do-while:
do {
System.out.println(“Count is: ” + count);
count++;
} while (count < 11);
switch-case:

数组:

二维数组:

对象:

类:
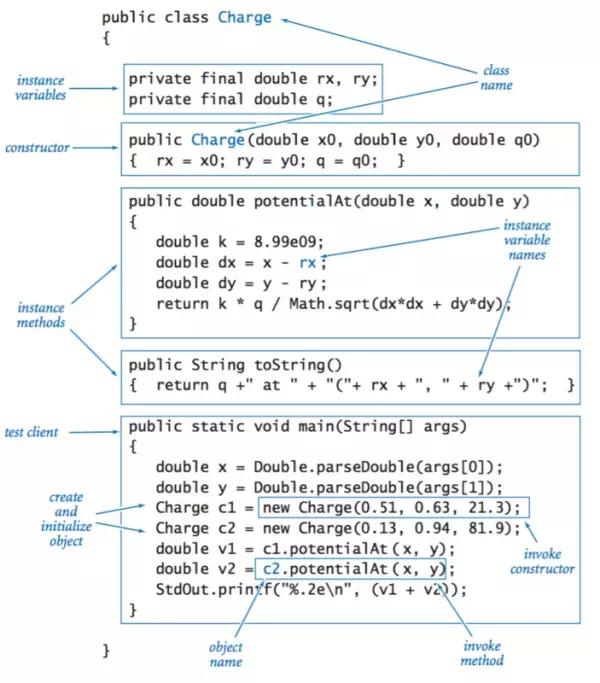
方法:

Java IDE 比较:

图片来自 Wikipedia
个人推荐 IntelliJ IDEA 并且对于 学生免费.
字符串 操作
字符串比较:
boolean result = str1.equals(str2);
boolean result = str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2);
搜索与检索:
int result = str1.indexOf(str2);
int result = str1.indexOf(str2,5);
String index = str1.substring(14);
单字节处理:
for (int i=0;i
字符串反转:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = “whatever string something”;
StringBuffer str1buff = new StringBuffer(str1);
String str1rev = str1buff.reverse(). toString ();
System.out.println(str1rev);
}
}
按单词的字符串反转:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = “reverse this string”;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
StringTokenizer strTok = new StringTokenizer(str1);
while(strTok.hasMoreTokens()){
stack.push(strTok.nextElement());
}
StringBuffer str1rev = new StringBuffer();
while(!stack.empty()){
str1rev.append(stack.pop());
str1rev.append(” “);
}
System.out.println(str1rev);
}
}
大小写转化:
String strUpper = str1.toUpperCase();
String strLower = str1.toLowerCase();
首尾空格移除:
String str1 = ” asdfsdf “;
str1.trim(); //asdfsdf
空格移除:
str1.replace(” “,””);
字符串转化为数组:
String str = “tim,kerry,timmy,camden”;
String[] results = str.split(“,”);
数据结构
重置数组大小:
int[] myArray = new int[10];
int[] tmp = new int[myArray.length + 10];
System.arraycopy(myArray, 0, tmp, 0, myArray.length);
myArray = tmp;
集合遍历:
for (Iterator it = map.entrySet().iterator();it.hasNext();){
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)it.next();
Object key = entry.getKey();
Object value = entry.getValue();
}
创建映射集合:
hashmap map = new HashMap();
map.put(key1,obj1);
map.put(key2,obj2);
map.put(key2,obj2);
数组排序:
int[] nums = {1,4,7,324,0,-4};
Arrays.sort(nums);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
列表排序:
List unsortList = new ArrayList();
unsortList.add(“CCC”);
unsortList.add(“111”);
unsortList.add(“AAA”);
Collections.sort(unsortList);
列表搜索:
int index = arrayList.indexOf(obj);
finding an object by value in a hashmap:
hashmap.containsValue(obj);
finding an object by key in a hashmap:
hashmap.containsKey(obj);
二分搜索:
int[] nums = new int[]{7,5,1,3,6,8,9,2};
Arrays.sort(nums);
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(nums,6);
System.out.println(“6 is at index: “+ index);
arrayList 转化为 array:
Object[] objects = arrayList.toArray();
将 hashmap 转化为 array:
Object[] objects = hashmap.entrySet().toArray();
时间与日期类型
打印时间与日期:
Date todaysDate = new Date(); //todays date
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat(“EEE, dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss”); //date format
String formattedDate = formatter.format(todaysDate);
System.out.println(formattedDate);
将日期转化为日历:
Date mDate = new Date();
Calendar mCal = Calendar. getInstance ();
mCal.setTime(mDate);
将 calendar 转化为 date:
Calendar mCal = Calendar.getInstance();
Date mDate = mDate.getTime();
字符串解析为日期格式:
public void StringtoDate(String x) throws ParseException{
String date = “March 20, 1992 or 3:30:32pm”;
DateFormat df = DateFormat.getDateInstance();
Date newDate = df.parse(date);
}
date arithmetic using date objects:
Date date = new Date();
long time = date.getTime();
time += 5*24*60*60*1000; //may give a numeric overflow error on IntelliJ IDEA
Date futureDate = new Date(time);
System.out.println(futureDate);
date arithmetic using calendar objects:
Calendar today = Calendar.getInstance();
today.add(Calendar.DATE,5);
difference between two dates:
long diff = time1 – time2;
diff = diff/(1000*60*60*24);
comparing dates:
boolean result = date1.equals(date2);
getting details from calendar:
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.get(Calendar.MONTH);
cal.get(Calendar.YEAR);
cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR);
cal.get(Calendar.WEEK_OF_YEAR);
cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH);
cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
cal.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
calculating the elapsed time:
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//times flies by..
long finishTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long timeElapsed = startTime-finishTime;
System.out.println(timeElapsed);
正则表达式
使用 REGEX 寻找匹配字符串:
String Pattern = “[TJ]im”;
Pattern regPat = Pattern.compile(pattern,Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
String text = “This is Jim and that’s Tim”;
Matcher matcher = regPat.matcher(text);
if (matcher.find()){
String matchedText = matcher.group();
System.out.println(matchedText);
}
替换匹配字符串:
String pattern = “[TJ]im”;
Pattern regPat = Pattern.compile(pattern,Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
String text = “This is jim and that’s Tim”;
Matcher matcher = regPat.matcher(text);
String text2 = matcher.replaceAll(“Tom”);
System.out.println(text2);
使用 StringBuffer 替换匹配字符串:
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(“My”);
Matcher m = p.matcher(“My dad and My mom”);
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
boolean found = m.find();
while(found){
m.appendReplacement(sb,”Our”);
found = m.find();
}
m.appendTail(sb);
System.out.println(sb);
打印所有匹配次数:
String pattern = “\sa(\w)*t(\w)*”; //contains “at”
Pattern regPat = Pattern.compile(pattern);
String text = “words something at atte afdgdatdsf hey”;
Matcher matcher = regPat.matcher(text);
while(matcher.find()){
String matched = matcher.group();
System.out.println(matched);
}
打印包含固定模式的行:
String pattern = “^a”;
Pattern regPat = Pattern.compile(pattern);
Matcher matcher = regPat.matcher(“”);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(“file.txt”));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine())!= null){
matcher.reset(line);
if (matcher.find()){
System.out.println(line);
}
}
匹配新行:
String pattern = “\d$”; //any single digit
String text = “line onen line twon line threen”;
Pattern regPat = Pattern.compile(pattern, Pattern.MULTILINE);
Matcher matcher = regPat.matcher(text);
while (matcher.find()){
System.out.println(matcher.group());
}
regex:
- beginning of a string: ^
- end of a string: $
- 0 or 1 times: ?
- 0 or more times: (*) //without brackets
- 1 or more times: +
- alternative characters: […]
- alternative patterns: |
- any character: .
- a digit: d
- a non-digit: D
- whitespace: s
- non-whitespace: S
- word character: w
- non word character: W
数字与数学操作处理
内建数据类型:

- byte: 8bits, Byte
- short: 16bits, Short
- long: 64bits, Long
- float: 32bits, Float
判断字符串是否为有效数字:
String str = “dsfdfsd54353%%%”;
try{
int result = Integer .parseInt(str);
}
catch (NumberFormatException e){
System.out.println(“not valid”);
}
比较 Double:
Double a = 4.5;
Double b= 4.5;
boolean result = a.equals(b);
if (result) System.out.println(“equal”);
rounding:
double doubleVal = 43.234234200000000234040324;
float floatVal = 2.98f;
long longResult = Math.round(doubleVal);
int intResult = Math.round(floatVal);
System.out.println(longResult + ” and ” + intResult); // 43 and 3
格式化数字:
double value = 2343.8798;
NumberFormat numberFormatter;
String formattedValue;
numberFormatter = NumberFormat.getNumberInstance();
formattedValue = numberFormatter.format(value);
System.out.format(“%s%n”,formattedValue); //2.343,88
格式化货币:
double currency = 234546457.99;
NumberFormat currencyFormatter;
String formattedCurrency;
currencyFormatter = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
formattedCurrency = currencyFormatter.format(currency);
System.out.format(“%s%n”,formattedCurrency); // $ 234.546.457,99
二进制、八进制、十六进制转换:
int val = 25;
String binaryStr = Integer.toBinaryString(val);
String octalStr = Integer.toOctalString(val);
String hexStr = Integer.toHexString(val);
随机数生成:
double rn = Math.random();
int rint = (int) (Math.random()*10); // random int between 0-10
System.out.println(rn);
System.out.println(rint);
计算三角函数:
double cos = Math.cos(45);
double sin = Math.sin(45);
double tan = Math.tan(45);
计算对数
double logVal = Math.log(125.5);
Math library:


输入输出操作:
从输入流读取:
//throw IOexception first
BufferedReader inStream = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String inline =””;
while (!(inline.equalsIgnoreCase(“quit”))){
System.out.println(“prompt> “);
inline=inStream.readLine();
}
格式化输出:
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
Formatter formatter = new Formatter(buffer, Locale.US);
formatter.format(“PI: “+Math.PI);
System.out.println(buffer.toString());
formatter format calls:

打开文件:
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(textFile.txt)); //for reading
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(textFile.txt)); //for writing
读取二进制数据:
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(fileName);
int offset = 0;
int bytesRead = is.read(bytes, ofset, bytes.length-offset);
文件随机访问:
File file = new File(something.bin);
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file,”rw”);
raf.seek(file.length());
读取 Jar/zip/rar 文件:
ZipFile file =new ZipFile(filename);
Enumeration entries = file.entries();
while(entries.hasMoreElements()){
ZipEntry entry = (ZipEntry) entries.nextElement();
if (entry.isDirectory()){
//do something
}
else{
//do something
}
}
file.close();
文件与目录
创建文件:
File f = new File(“textFile.txt”);
boolean result = f.createNewFile();
文件重命名:
File f = new File(“textFile.txt”);
File newf = new File(“newTextFile.txt”);
boolean result = f.renameto(newf);
删除文件:
File f = new File(“somefile.txt”);
f.delete();
改变文件属性:
File f = new File(“somefile.txt”);
f.setReadOnly(); // making the file read only
f.setLastModified(desired time);
获取文件大小:
File f = new File(“somefile.txt”);
long length = file.length();
判断文件是否存在:
File f = new File(“somefile.txt”);
boolean status = f.exists();
移动文件:
File f = new File(“somefile.txt”);
File dir = new File(“directoryName”);
boolean success = f.renameTo(new File(dir, file.getName()));
获取绝对路径:
File f = new File(“somefile.txt”);
File absPath = f.getAbsoluteFile();
判断是文件还是目录:
File f = new File(“somefile.txt”);
boolean isDirectory = f.isDirectory();
System.out.println(isDirectory); //false
列举目录下文件:
File directory = new File(“users/ege”);
String[] result = directory.list();
创建目录:
boolean result = new File(“users/ege”).mkdir();
网络客户端
服务器连接:
String serverName = “www.egek.us”;
Socket socket = new Socket(serverName, 80);
System.out.println(socket);
网络异常处理:
try {
Socket sock = new Socket(server_name, tcp_port);
System.out.println(“Connected to ” + server_name);
sock.close( );
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.err.println(server_name + ” Unknown host”);
return;
} catch (NoRouteToHostException e) {
System.err.println(server_name + ” Unreachable” );
return;
} catch (ConnectException e) {
System.err.println(server_name + ” connect refused”);
return;
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
System.err.println(server_name + ‘ ‘ + e.getMessage( ));
return;
}
包与文档
创建包:
package com.ege.example;
使用 JavaDoc 注释某个类:
javadoc -d homehtml
-sourcepath homesrc
-subpackages java.net
Jar 打包:
jar cf project.jar *.class
运行 Jar:
java -jar something.jar
排序算法
- Bubble Sort
- Linear Search
- Binary Search
- Selection Sort
- Insertion Sort
Over here
- Java


