前言
这一篇文章将讲述 redis 中的sortedset类型命令,同样也是通过demo来讲述,其他部分这里就不在赘述了。
案例
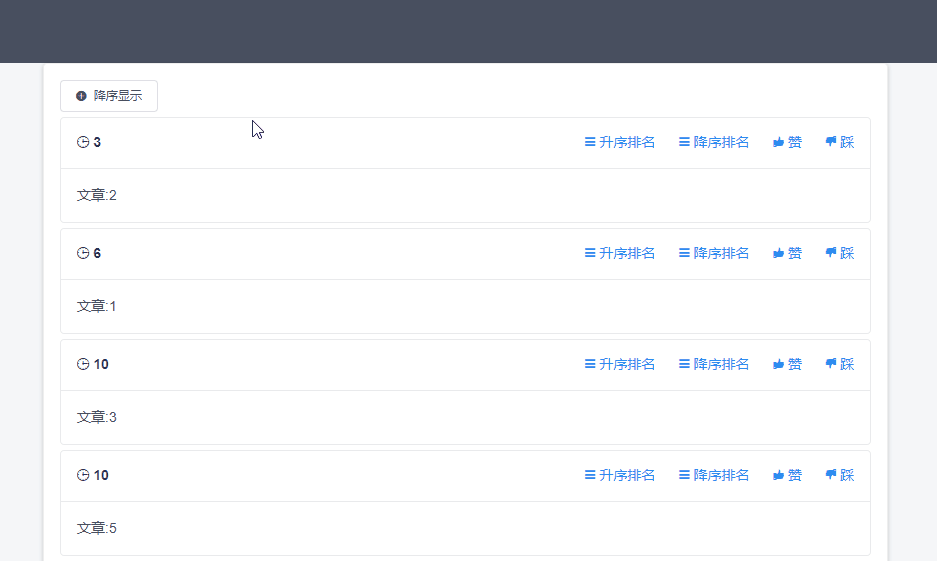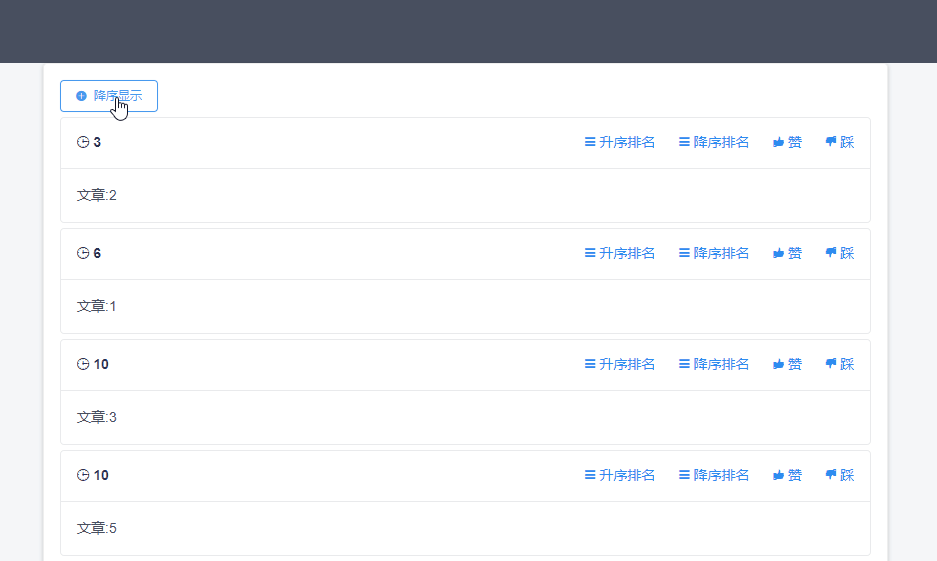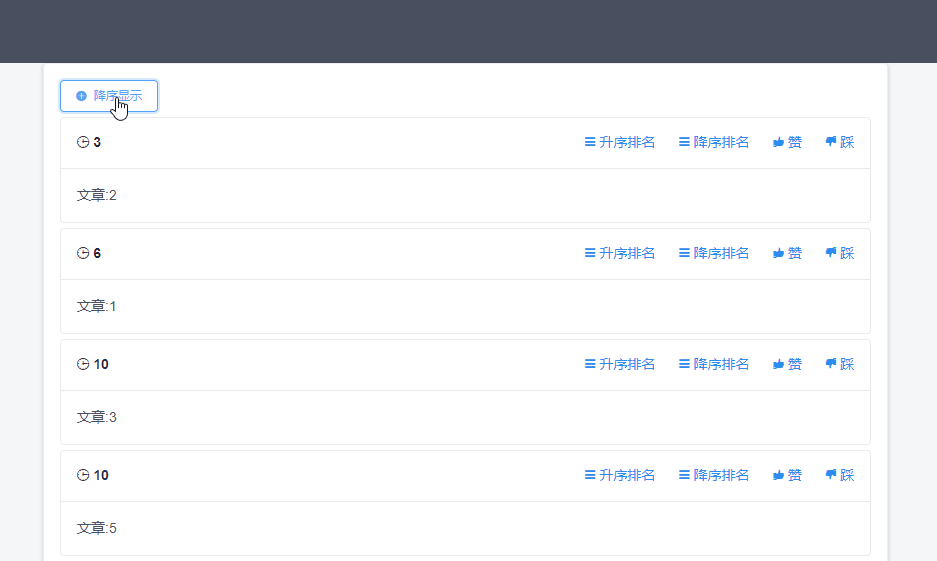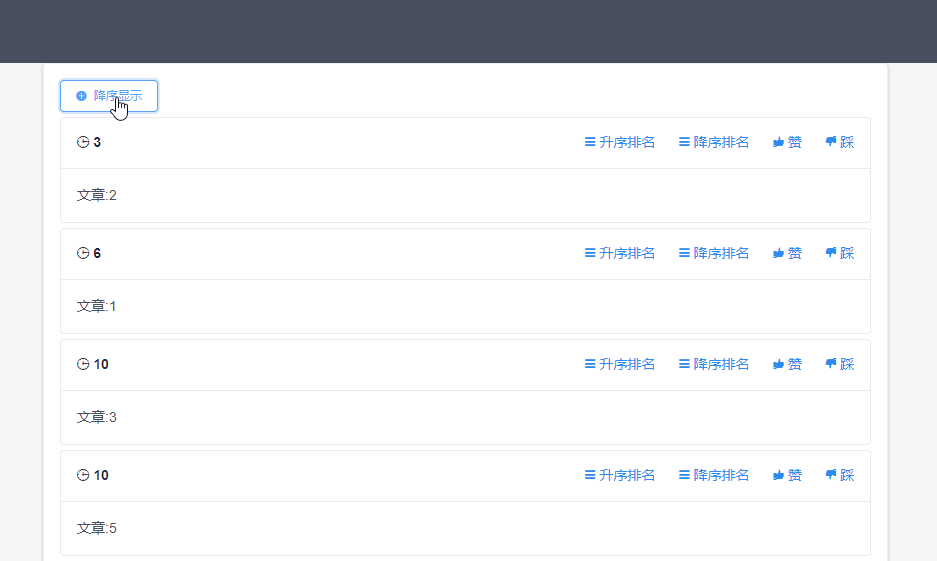
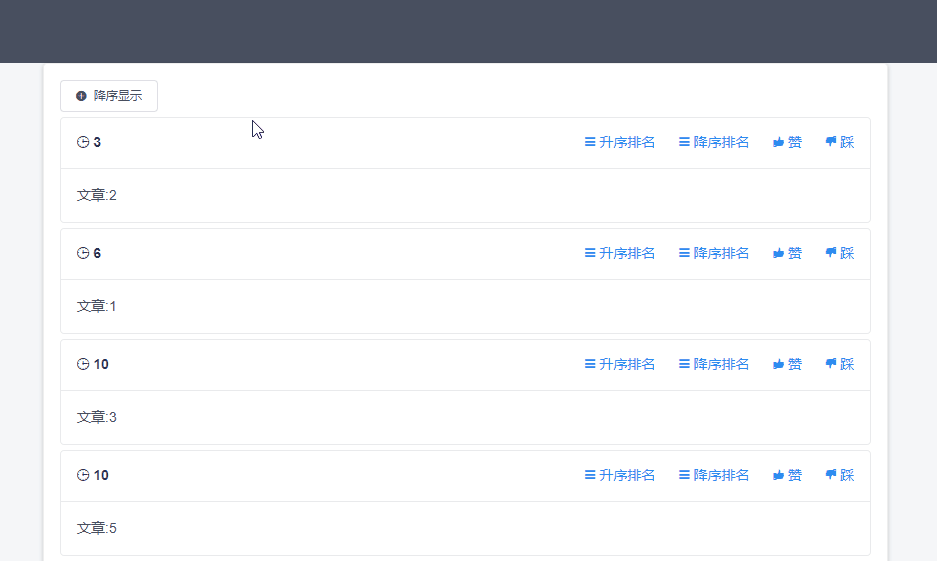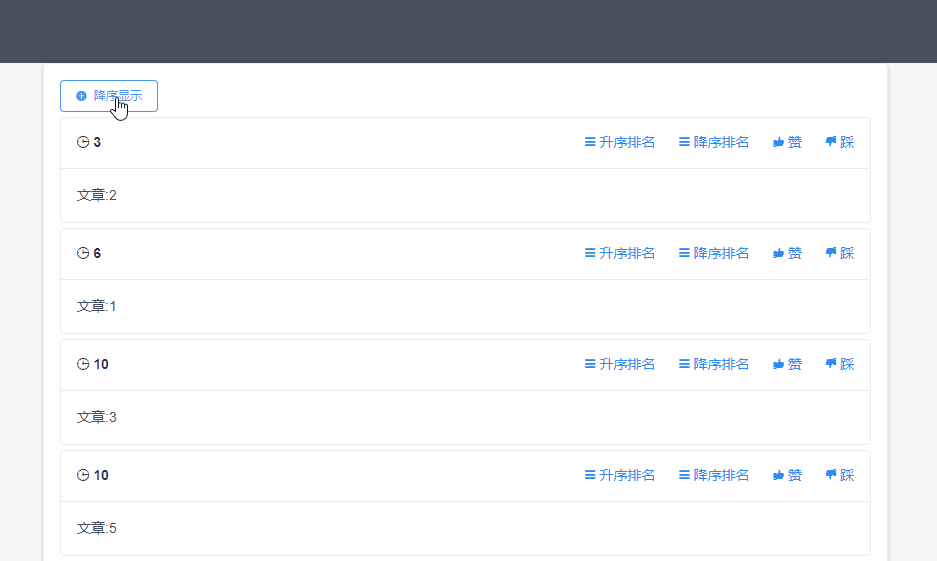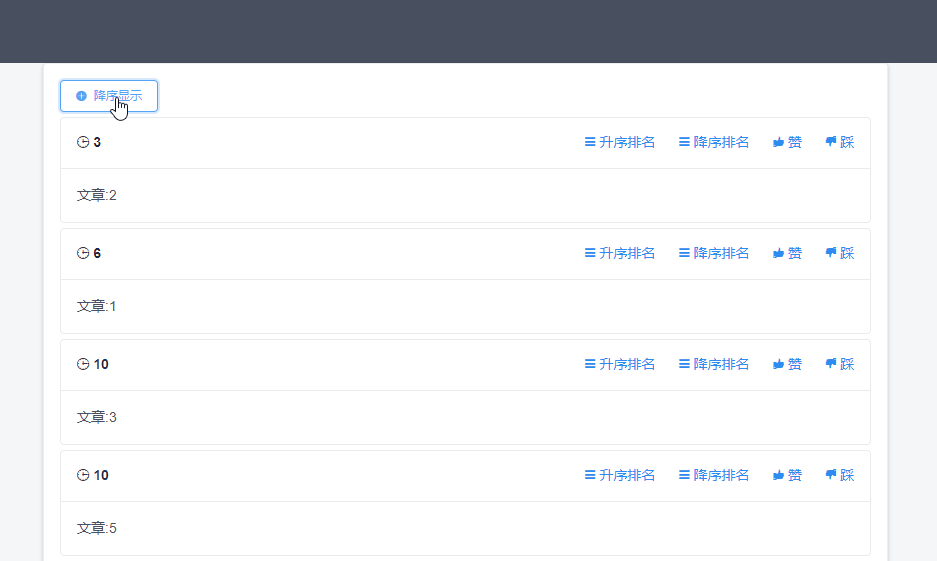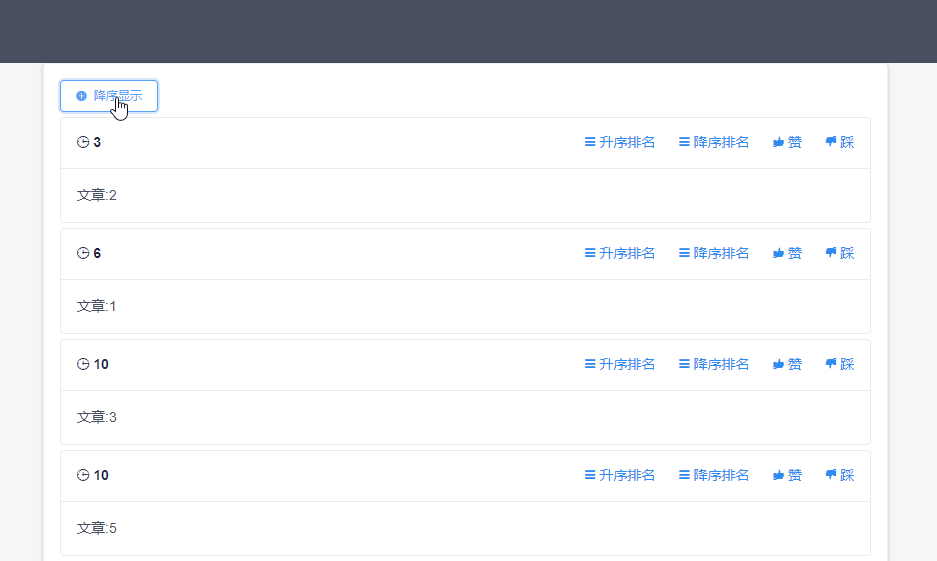
demo功能是文章点赞排名等等,整个demo的大致页面如下。
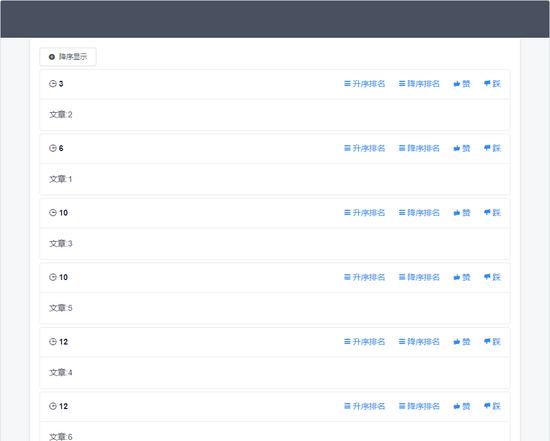
准备工作
首先定义一个存储文章的key
redis操作对象
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
//string 命令操作对象
private ValueOperations valueOperations;
//zset 命令操作对象
private ZSetOperations zSetOperations;
sortedset在Redis中的结构可以看下图(图片来源于Redis in Action)。

列表查询
@RequestMapping(value = “/getList/{sortType}”, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Set getList(@PathVariable String sortType) {
//如果没有数据,则添加10条数据
if (zSetOperations.size(ZSET_KEY) == 0){
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
zSetOperations .add(ZSET_KEY,”文章:”+i, (int)(Math.random()*10+i));
}
}
//ASC根据分数从小到大排序,DESC反之
if (“ASC”.equals(sortType)){
return zSetOperations .rangeWithScores(ZSET_KEY, 0, -1);
} else {
return zSetOperations .reverseRangeWithScores(ZSET_KEY, 0, -1);
}
}
这里为了省去一个个添加数据的麻烦,就在获取列表数据中加了个判断。当文章数据为0时,默认添加10条数据,设置随机score加上所在的索引。
然后根据url中的参数sortType来决定返回的数据是按照分数升序还是降序排序。功能效果如下
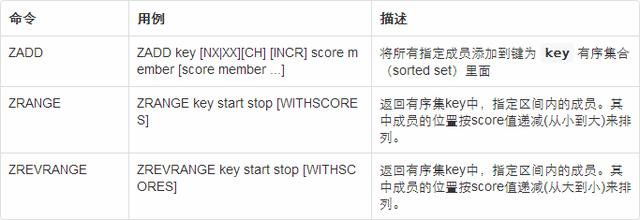
命令介绍
赞或踩
java代码如下
@RequestMapping(value = “/star”, method = RequestMethod.POST)
public boolean starOrUnStar(String member , String type ) {
if (“UP”.equals( type )){
zSetOperations.incrementScore(ZSET_KEY, member , 1);
} else {
zSetOperations.incrementScore(ZSET_KEY, member , -1);
}
return true ;
}
根据type决定是否加减分数,当type为UP时表示赞,为其他(DOWN)时表示踩。功能效果如下
命令介绍

升降序排名
java代码如下
@RequestMapping(value = “/rank/{type}/{member}”, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Long rank(@PathVariable String member , @PathVariable String type ) {
Long rank = null ;
if (“ASC”.equals( type )){
rank = zSetOperations.rank(ZSET_KEY, member );
} else {
rank = zSetOperations.reverseRank(ZSET_KEY, member );
}
return rank;
}
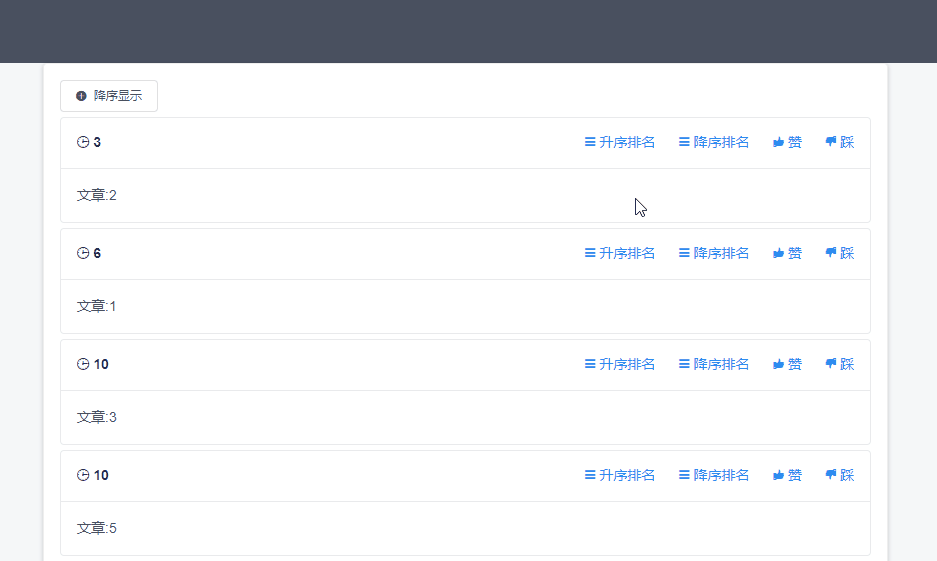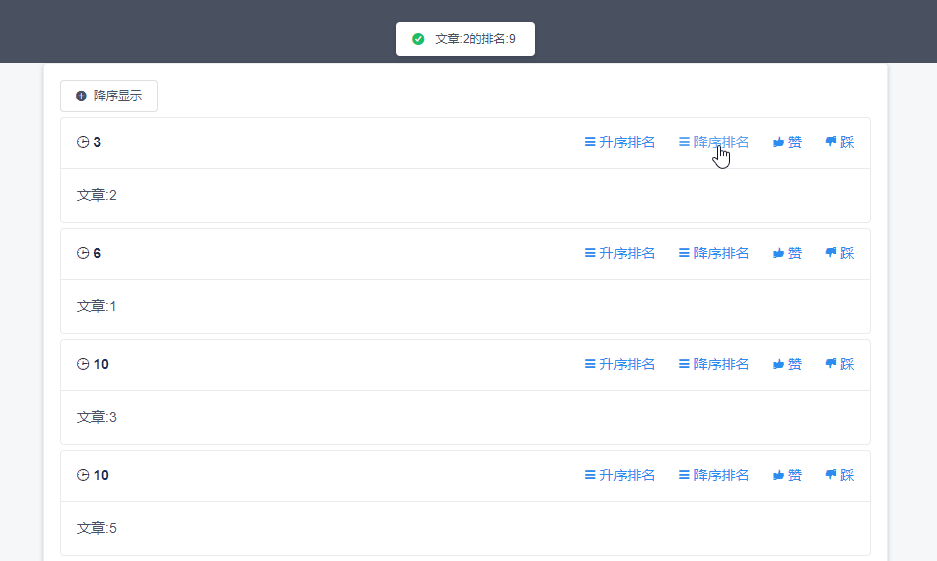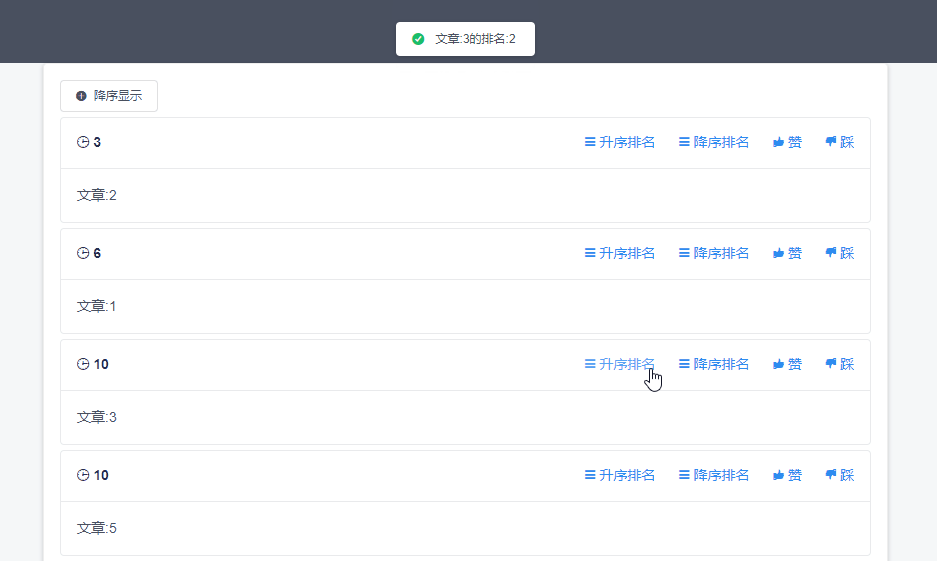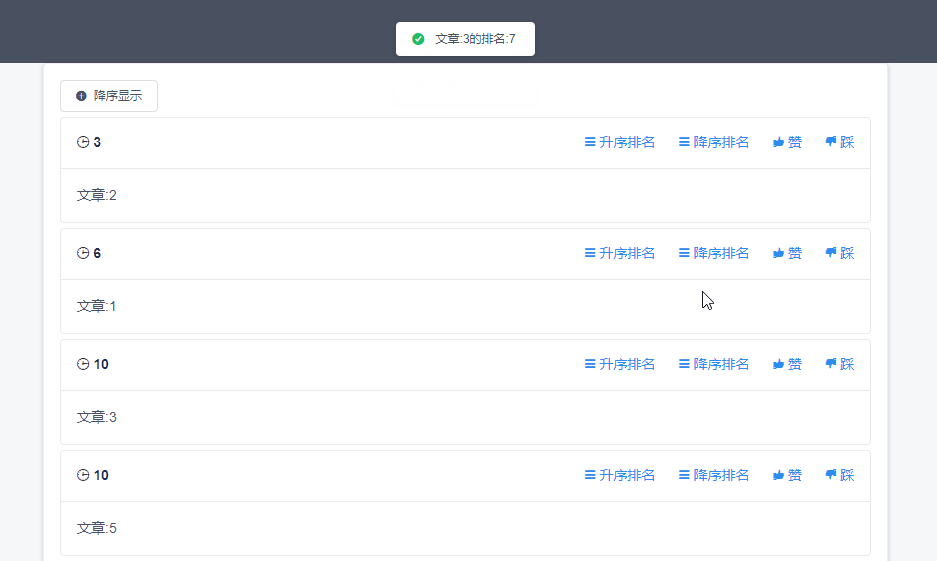
根据type决定是升序排名还是降序排名,如果是ASC则调用rank方法获取升序排名,其他则调用reverseRank获取降序排名。与下方redis命令类似
ZRANK articleList “文章1”
ZREVRANK articleList “文章1”
页面效果图如下
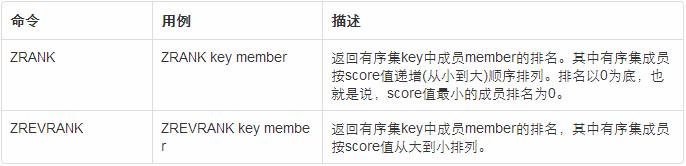
命令介绍
其他命令
获取属性
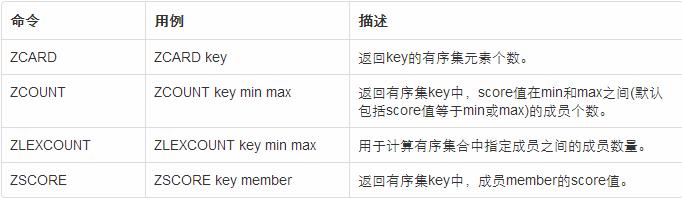
ZCARD命令
返回key的有序集元素个数。
ZCARD key
返回值:key存在的时候,返回有序集的元素个数,否则返回0。
redis客户端执行的命令如下
zadd zCardKey 1 one
zcard zCardKey
下面是java代码
@ Test
public void zCard() {
jedis .zadd(“zCardKey”,1, “one”);
jedis .zadd(“zCardKey”,2, “two”);
System .out.println(jedis.zcard(“zCardKey”));
System .out.println(zSetOperations.size(“zCardKey”));
}
ZCOUNT命令
返回有序集key中,score值在min和max之间(默认包括score值等于min或max)的成员数量。
ZCOUNT key min max
返回值:指定分数范围的元素个数。
redis客户端执行的命令如下
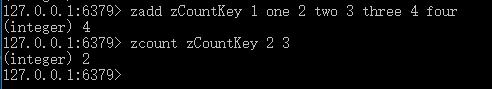
zadd zCountKey 1 one 2 two 3 three 4 four
zcount zCountKey 2 3
执行结果如下
下面是java代码
@Test
public void zCount() {
jedis .zadd(“zCountKey”,1, “one”);
jedis .zadd(“zCountKey”,2, “two”);
jedis .zadd(“zCountKey”,3, “three”);
jedis .zadd(“zCountKey”,4, “four”);
System .out.println(jedis.zcount(“zCountKey”,2, 3));
System .out.println(zSetOperations.count(“zCountKey”,2, 3));
}
ZLEXCOUNT命令
计算有序集合中指定成员之间的成员数量(按成员字典正序排序),可以使用 – 和 + 表示score最小值和最大值
ZLEXCOUNT key min max
redis客户端执行的命令如下
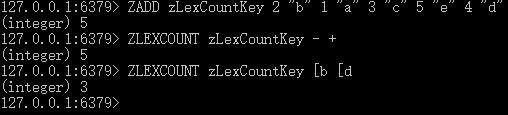
ZADD zLexCountKey 2 “b” 1 “a” 3 “c” 5 “e” 4 “d”
ZLEXCOUNT zLexCountKey – +
ZLEXCOUNT zLexCountKey [b [d
执行结果如下
下面是java代码
@Test
public void zLexCount () {
zSetOperations. add (“zLexCountKey”, “b”, 2);
zSetOperations. add (“zLexCountKey”, “a”, 1);
zSetOperations. add (“zLexCountKey”, “c”, 3);
zSetOperations. add (“zLexCountKey”, “e”, 5);
zSetOperations. add (“zLexCountKey”, “d”, 4);
System. out .println(jedis.zlexcount(“zLexCountKey”, “-“, “+”));
System. out .println(jedis.zlexcount(“zLexCountKey”, “[b”, “[d”));
}
ZSCORE命令
返回有序集key中,成员member的score值。
ZSCORE key member
返回值:成员member的score值
redis客户端执行的命令如下
zadd zScoreKey 1 one
ZSCORE zScoreKey one
下面是java代码
@Test
public void zScore () {
jedis.zadd(“zScoreKey”,1, “one”);
System. out .println(jedis.zscore(“zScoreKey”, “one”));
System. out .println(zSetOperations.score(“zScoreKey”, “one”));
}
获取成员

ZRANGEBYLEX命令
返回指定成员区间内的成员,按成员字典正序排序。
ZRANGEBYLEX key min max [LIMIT offset count]
返回值:指定成员范围的元素列表。
redis客户端执行的命令如下
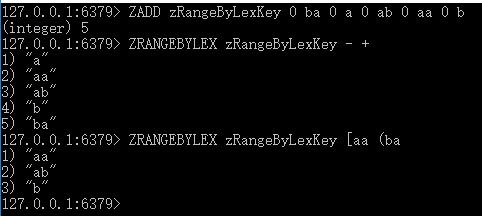
ZADD zRangeByLexKey 0 ba 0 a 0 ab 0 aa 0 b
ZRANGEBYLEX zRangeByLexKey – +
ZRANGEBYLEX zRangeByLexKey [aa ( ba
执行结果如下
下面是java代码
@Test
public void zRangeByLex () {
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByLexKey”, “ba”, 0);
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByLexKey”, “a”, 0);
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByLexKey”, “ab”, 0);
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByLexKey”, “aa”, 0);
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByLexKey”, “b”, 0);
System. out .println(jedis.zrangeByLex(“zRangeByLexKey”, “-“, “+”));
RedisZSetCommands.Range range = new RedisZSetCommands.Range();
range.gte(“aa”);
range.lt(“ba”);
System. out .println(zSetOperations.rangeByLex(“zRangeByLexKey”,range));
}
ZRANGEBYSCORE命令
获取score在范围之内的数据。min和max可以是-inf和+inf
ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max [WITHSCORES]“[LIMIT offset count]
redis客户端执行的命令如下
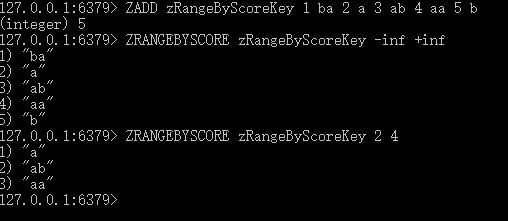
ZADD zRangeByScoreKey 1 ba 2 a 3 ab 4 aa 5 b
ZRANGEBYSCORE zRangeByScoreKey -inf +inf
ZRANGEBYSCORE zRangeByScoreKey 2 4
执行结果如下
下面是java代码
@Test
public void zRangeByScore () {
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByScoreKey”, “ba”, 1);
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByScoreKey”, “a”, 2);
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByScoreKey”, “ab”, 3);
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByScoreKey”, “aa”, 4);
zSetOperations. add (“zRangeByScoreKey”, “b”, 5);
System. out .println(jedis.zrangeByScore(“zRangeByScoreKey”, “-inf”, “+inf”));
RedisZSetCommands.Range range = new RedisZSetCommands.Range();
System. out .println(zSetOperations.rangeByScore(“zRangeByScoreKey”, 2, 4));
}
移除相关命令
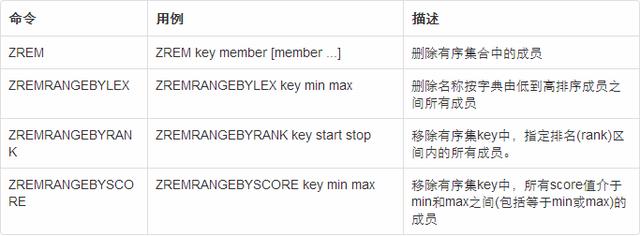
ZREM命令
ZREM key member [member …]
返回值:有序集合中删除的成员个数
redis客户端执行的命令如下
ZADD zRemKey 1 “one” 2 “two” 3 “three”
ZREM zRemKey one
ZRANGE zRemKey 0 -1
执行结果如下

下面是java代码
@Test
public void zRem () {
zSetOperations. add (“zRemKey”, “one”, 1);
zSetOperations. add (“zRemKey”, “two”, 2);
zSetOperations. add (“zRemKey”, “three”, 3);
//jedis.zrem(“zRemKey”, “one”);
zSetOperations. remove (“zRemKey”, “one”);
System. out .println(zSetOperations.range(“zRemKey”, 0 , -1));
}
交并集

ZINTERSTORE命令
计算给定的numkeys个有序集合的交集,并且把结果放到destination中。
在给定要计算的key和其它参数之前,必须先给定key个数(numberkeys)。
默认情况下,结果中一个元素的分数是有序集合中该元素分数之和,前提是该元素在这些有序集合中都存在。因为交集要求其成员必须是给定的每个有序集合中的成员,结果集中的每个元素的分数和输入的有序集合个数相等。
对于WEIGHTS和AGGREGATE参数的描述,参见命令ZUNIONSTORE。
如果destination存在,就把它覆盖。
ZINTERSTORE destination numkeys key [key …] [WEIGHTS weight [weight …]] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]
返回值:结果有序集合destination中元素个数。
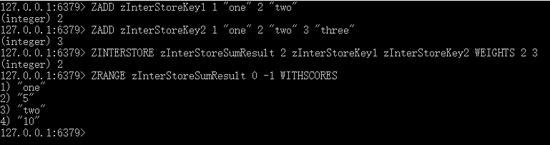
redis客户端执行的命令如下
ZADD zInterStoreKey1 1 “one” 2 “two”
ZADD zInterStoreKey2 1 “one” 2 “two” 3 “three”
ZINTERSTORE zInterStoreSumResult 2 zInterStoreKey1 zInterStoreKey2 WEIGHTS 2 3
ZRANGE zInterStoreSumResult 0 -1 WITHSCORES
执行结果如下
下面是java代码
@Test
public void zInterStore () {
zSetOperations. add (“zInterStoreKey1”, “one”, 1);
zSetOperations. add (“zInterStoreKey1”, “two”, 2);
zSetOperations. add (“zInterStoreKey2”, “one”, 1);
zSetOperations. add (“zInterStoreKey2”, “two”, 2);
zSetOperations. add (“zInterStoreKey2”, “three”, 3);
ZParams zParams = new ZParams();
zParams.weightsByDouble(2, 3);
zParams.aggregate(ZParams.Aggregate.SUM);
jedis.zinterstore(“zInterStoreSumResult”, zParams, “zInterStoreKey1”, “zInterStoreKey2”);
printTuple(“zInterStoreSumResult”, jedis.zrangeWithScores(“zInterStoreSumResult”, 0, -1));
}
ZUNIONSTORE命令
计算给定的numkeys个有序集合的并集,并且把结果放到destination中。
WEIGHTS参数相当于权重,默认就是1,可以给不同的key设置不同的权重
AGGREGATE参数默认使用的参数SUM,还可以选择MIN或者MAX。这个参数决定结果集的score是取给定集合中的相加值、最小值还是最大值
ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key [key …] [WEIGHTS weight [weight …] ] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]
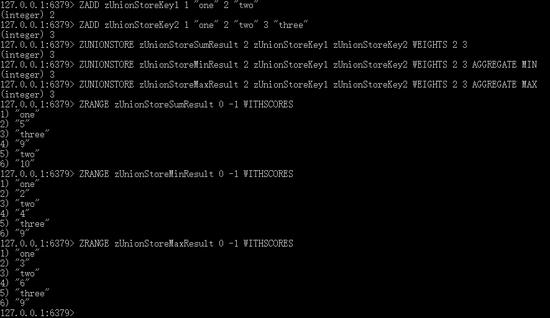
redis客户端执行的命令如下
ZADD zUnionStoreKey1 1 “one” 2 “two”
ZADD zUnionStoreKey2 1 “one” 2 “two” 3 “three”
ZUNIONSTORE zUnionStoreSumResult 2 zUnionStoreKey1 zUnionStoreKey2 WEIGHTS 2 3
ZUNIONSTORE zUnionStoreM in Result 2 zUnionStoreKey1 zUnionStoreKey2 WEIGHTS 2 3 AGGREGATE MIN
ZUNIONSTORE zUnionStoreMaxResult 2 zUnionStoreKey1 zUnionStoreKey2 WEIGHTS 2 3 AGGREGATE MAX
*
ZRANGE zUnionStoreSumResult 0 -1 WITHSCORES
ZRANGE zUnionStoreM in Result 0 -1 WITHSCORES
ZRANGE zUnionStoreMaxResult 0 -1 WITHSCORES
执行结果如下
下面是java代码
@Test
public void zUnionStore () {
zSetOperations. add (“zUnionStoreKey1”, “one”, 1);
zSetOperations. add (“zUnionStoreKey1”, “two”, 2);
zSetOperations. add (“zUnionStoreKey2”, “one”, 1);
zSetOperations. add (“zUnionStoreKey2”, “two”, 2);
zSetOperations. add (“zUnionStoreKey2”, “three”, 3);
ZParams zParams = new ZParams();
zParams.weightsByDouble(2, 3);
zParams.aggregate(ZParams.Aggregate.SUM);
jedis.zunionstore(“zUnionStoreSumResult”, zParams, “zUnionStoreKey1”, “zUnionStoreKey2”);
//求最小值
zParams.aggregate(ZParams.Aggregate.MIN);
jedis.zunionstore(“zUnionStoreMinResult”, zParams, “zUnionStoreKey1”, “zUnionStoreKey2”);
//求最大值
zParams.aggregate(ZParams.Aggregate.MAX);
jedis.zunionstore(“zUnionStoreMaxResult”, zParams, “zUnionStoreKey1”, “zUnionStoreKey2”);
//spring
zSetOperations.unionAndStore(“zUnionStoreKey1”, “zUnionStoreKey2”, “zUnionStoreResult”);
printTuple(“zUnionStoreSumResult”, jedis.zrangeWithScores(“zUnionStoreSumResult”, 0, -1));
printTuple(“zUnionStoreMinResult”, jedis.zrangeWithScores(“zUnionStoreMinResult”, 0, -1));
printTuple(“zUnionStoreMaxResult”, jedis.zrangeWithScores(“zUnionStoreMaxResult”, 0, -1));
printTuple(“zUnionStoreResult”, jedis.zrangeWithScores(“zUnionStoreResult”, 0, -1));
}
还是那句话建议学习的人最好每个命令都去敲下,加深印象。
纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行。————出自《冬夜读书示子聿》
欢迎大家关注转发支持一波~
关注我:转发+私信回复“架构资料”获取往期Java高级架构资料、源码、笔记、视频
Dubbo、Redis、设计模式、Netty、zookeeper、Spring cloud、分布式、
高并发等架构技术


