一. 线性表
线性表( linear list ) 是 n 个具有 相同特性的数据元素 的 有限序列 。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见 的线性表: 顺序表、 链表 、栈、队列、 字符串 …
线性表在 逻辑上是线性结构 ,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上 并不一定是连续的 ,线性表在物理上存储 时,通常 以数组和链式结构 的形式存储。
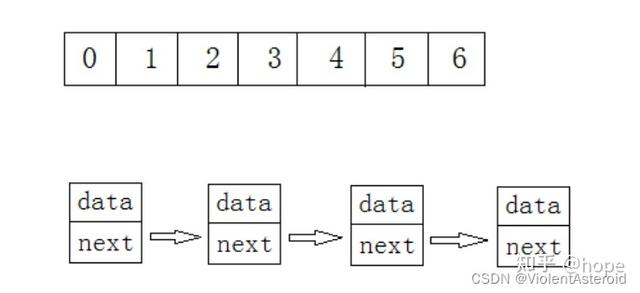
二.顺序表
1.概念及结构
顺序表 是用一段 物理地址连续 的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用 数组 存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
而顺序表一般可以分为两类: 静态顺序表、动态顺序表

2.顺序表的实现
首先我们将顺序表的成员属性以及构造函数写好,接下来实现具体接口
public class MyArrayList {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;//有效的数据个数,默认值为0
public MyArrayList() {//初始化一个数组,容量为5
this.elem = new int[5];
}
}
打印顺序表
只需要遍历完数组,然后将其打印出来即可
具体的代码实现:
// 打印顺序表
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize ; i++) {
System.out.print(elem[i]+” “);
}
System.out.println();
}
获取顺序表的有效长度
有效长度就是已经用过的元素,返回usedSize即可
具体的代码实现:
// 获取顺序表的有效数据长度
public int size() {
return usedSize;
}
在pos位置新增元素
具体的操作分为四步:
- 判断pos位置是否合法,即pos既不能小于0,也不能大于有效数据个数
- 判断顺序表是否已满,如果满了,需要Arrays. copy Of()进行扩容
- 将pos后的元素依次后移,即 elem[i+1]=elem[i]
- 将目标元素data放入pos下标对应位置,即elem[pos]=data
具体的代码实现:
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
//1.判断pos位置是否合法
if (pos<0 || pos>usedSize){
System.out.println(“pos位置不合法”);
return;
}
//2.判断usedSize是否已满
if (isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//3.开始挪数据,并且给pos位置赋值
for (int i = usedSize-1; i >= pos ; i–) {
elem[i+1]=elem[i];//把i下标的值给i+1
}
this.elem[pos]=data;
this.usedSize++;//说明存放成功
}
public boolean isFull(){
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
判断是否包含某个元素
只需要传入需要查找的元素toFind,然后遍历查找即可
具体的代码实现:
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize ; i++) {
if (this.elem[i]==toFind)
return true;
}
return false;
}
查找某个元素对应的位置
跟上一个操作一样,使用遍历查找到元素后,返回其下标即可
具体的代码实现:
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int search(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if (this.elem[i]==toFind)
return i;//找到了返回i下标
}
return -1; //找不到返回-1,因为数组没有负数下标
}
获取/查找pos位置的元素
凡是传入pos位置,我们都需要判断pos是否合法,也要查看顺序表是否为空,如果合法且不为空直接返回该下标对应的元素即可
具体的代码实现:
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int getPos(int pos) {
if (pos<0 || pos>this.usedSize){
System.out.println(“pos位置不合法”);
return -1;//说明pos位置不合法
}
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println(“顺序表为空”);
return -1;
}
return this.elem[pos];//返回pos位置的值
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize==0;
}
给pos位置的元素设为value
依然先判断pos位置是否合法,再判断顺序表是否为空,如果合法且不为空,则将value赋值给pos下标对应的元素
具体的代码实现:
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为/更新为 value
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
//还是要先判断pos位置的合法性
if (pos<0 || pos>usedSize){
System.out.println(“pos位置不合法”);
return;
}
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println(“顺序表为空”);
return ;
}
this.elem[pos] = value;//将pos位置的元素更新为value
}
删除第一次出现的关键字key
具体步骤如下:
- 判断顺序表是否为空(除了增加元素是判断顺序表是否已满,其他的都是判断是否为空)
- 调用我们上边写的 search函数 ,看是否存在该元素
- 如果存在,则从该元素起,将后面的元素往前挪,将要删除的元素覆盖
具体的代码实现如下:
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println(“顺序表为空”);
return;
}
int index = search(toRemove);
if (index==-1) {
System.out.println(“没有你要删除的数字”);
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < usedSize-1; i++) {
this.elem[i]=this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize–;
//this.elem[usedSize]=null; 如果数组当中是引用类型,则要将其置为空
}
清空顺序表
清空顺序表,只需要把有效长度置于0即可
具体的代码实现:
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
this.usedSize = 0;
}
3.顺序表的优、缺点
优点:由于顺序表是物理和 逻辑上都连续的 ,可以快速查找到当前数据,时间复杂度为O(1)
缺点:
- 删除和插入数据的时候,都需要移动数据,时间复杂度为O(N)
- 扩容也是问题, 增容 一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入5个数据,无后续数据插入,那么就浪费了95个数据空间
那么顺序表的缺点怎么才能解决呢?链表很好的解决了顺序表的缺点,随用随取,需要空间的时候就new一个结点。需要注意的是,链表是 物理上不连续 ,而 逻辑上连续 。
三.顺序表的实现代码汇总
public class MyArrayList {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[5];
}
// 打印顺序表
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize ; i++) {
System.out.print(elem[i]+” “);
}
System.out.println();
}
// 获取顺序表的有效数据长度
public int size() {
return usedSize;
}
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
//1.判断pos位置是否合法
if (pos<0 || pos>usedSize){
System.out.println(“pos位置不合法”);
return;
}
//2.判断usedSize是否已满
if (isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//3.开始挪数据,并且给pos位置赋值
for (int i = usedSize-1; i >= pos ; i–) {
elem[i+1]=elem[i];//把i下标的值给i+1
}
this.elem[pos]=data;
this.usedSize++;//说明存放成功
}
public boolean isFull(){
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize ; i++) {
if (this.elem[i]==toFind)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int search(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if (this.elem[i]==toFind)
return i;//找到了返回i下标
}
return -1; //找不到返回-1,因为数组没有负数下标
}
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int getPos(int pos) {
if (pos<0 || pos>this.usedSize){
System.out.println(“pos位置不合法”);
return -1;//说明pos位置不合法
}
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println(“顺序表为空”);
return -1;
}
return this.elem[pos];//返回pos位置的值
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize==0;
}
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为/更新为 value
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
//还是要先判断pos位置的合法性
if (pos<0 || pos>usedSize){
System.out.println(“pos位置不合法”);
return;
}
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println(“顺序表为空”);
return ;
}
this.elem[pos] = value;//将pos位置的元素更新为value
}
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println(“顺序表为空”);
return;
}
int index = search(toRemove);
if (index==-1) {
System.out.println(“没有你要删除的数字”);
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < usedSize-1; i++) {
this.elem[i]=this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize–;
//this.elem[usedSize]=null; 如果数组当中是引用类型,则要将其置为空
}
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
this.usedSize = 0;
}
}


