上篇文章我们已经详细的介绍了数据结构跳表的原理,并通过LeetCode第1206题(难度:困难)来实战了一下跳表的实现。
今天我们继续为大家带来JDK1.8中对跳表的支持实现源码解析,即: java .util.concurrent包下的ConcurrentSkipListMap,本文代码较多,篇幅较长,需要大家对着源码耐心阅读。
ConcurrentSkipListMap类继承关系
我们先利用Idea自带的Diagrams–>show diagram…来看一下ConcurrentSkipListMap的继承实现关系图:
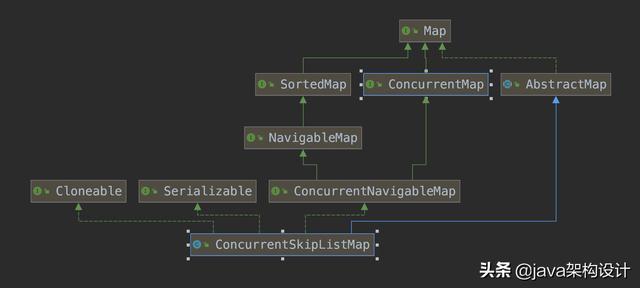
根据上图可以很清晰的看到ConcurrentSkipListMap继承了 abstract Map类,并实现了ConcurrentNavigableMap接口,而ConcurrentNavigableMap接口又继承了NavigableMap接口和ConcurrentMap接口,NavigableMap接口又继承了SortedMap接口,SortedMap接口和ConcurrentMap接口类均继承自Map接口。
//ConcurrentSkipListMap
public class ConcurrentSkipListMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements ConcurrentNavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
}
//ConcurrentNavigableMap
public interface ConcurrentNavigableMap<K,V>
extends ConcurrentMap<K,V>, NavigableMap<K,V> {
}
//NavigableMap
public interface NavigableMap<K,V> extends SortedMap<K,V> {
}
//SortedMap
public interface SortedMap<K,V> extends Map<K,V> {
} Map接口相信大家一定不陌生,它主要定义了一个无序的 Key-Value 键值对数据存储结构,典型的实现就是 HashMap ,也是我们平时开发使用最频繁的数据结构之一了,而SortedMap则是针对Map接口的增强,定义了有序的Key-Value键值对数据存储结构,NavigableMap接口则在SortedMap的基础上增强了一些实现,例如根据指定Key返回最接近项、按升序/降序返回所有键的视图等功能:
public interface NavigableMap<K,V> extends SortedMap<K,V> {
//返回小于给定key的最大的Entry,如果没有则返回null
Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key);
//返回小于给定key的最大的Key,如果没有则返回null
K lowerKey(K key);
//返回小于等于给定key的最大的Entry,如果没有则返回null
Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key);
//返回小于等于给定key的最大的Key,如果没有则返回null
K floorKey(K key);
//升序返回所有键的视图
NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet();
//降序返回所有键的视图
NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet();
} NavigableMap大家可能比较陌生,但是它的一个实现类大家肯定比较熟悉,那就是TreeMap,面试时候相信大家一定遇到过经典面试题: 说说 Hashtable 、HashMap、TreeMap的区别? TreeMap是一个有序的Map,他的底层基于 红黑树 实现。
上面为大家整体介绍了一下Map家庭成员的整体架构信息,此时我们可以知道ConcurrentSkipListMap类是一个并发安全的、有序的基于跳表实现的Map。接下来让我们走进ConcurrentSkipListMap的源码世界。
ConcurrentSkipListMap源码剖析
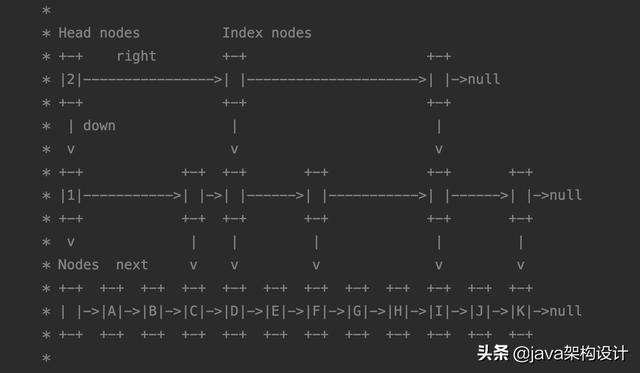
上图截取自ConcurrentSkipListMap源码里的javadoc注释,他有三种类型的节点:
- 原始 链表 普通节点:Nodes;
- 头节点:Head nodes;
- 索引节点:Index nodes;
原始链表普通节点定义
/**
* Nodes hold keys and values, and are singly linked in sorted
* order, possibly with some intervening marker Node s. The list is
* headed by a dummy node accessible as head.node. The value field
* is declared only as Object because it takes special non-V
* values for marker and header nodes.
*/ static final class Node<K,V> {
final K key;
volatile Object value;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
/**
* 构造方法 :创建一个常规普通节点
*/ Node(K key, Object value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
/**
* 构造方法:创建一个标记节点,标记节点用于并发删除时候使用
*/ Node(Node<K,V> next) {
this.key = null;
this.value = this;
this.next = next;
}
/**
* CAS设置节点的value
*/ boolean casValue(Object cmp, Object val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, valueOffset, cmp, val);
}
/**
* CAS设置节点的next节点
*/ boolean casNext(Node<K,V> cmp, Node<K,V> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);
}
/**
* 判断当前节点是否为标记节点
*/ boolean isMarker() {
return value == this;
}
/**
* 判断当前节点是否为原始链表的头节点
*/ boolean isBaseHeader() {
return value == BASE_HEADER;
}
/**
* CAS操作在当前节点后面插入一个标记节点
* @param f 当前节点的后继节点
* @return true成功,false失败
*/ boolean appendMarker(Node<K,V> f) {
return casNext(f, new Node<K,V>(f));
}
/**
* 帮助删除当前节点,这个方法很绕,即使下面有每句代码的注释
* @param b 前置节点
* @param f 后置节点
*/ void helpDelete(Node<K,V> b, Node<K,V> f) {
//如果f是当前节点的next节点 并且 当前节点是节点b的next节点
//意味着没有并发安全问题
if (f == next && this == b.next) {
//如果当前节点是尾节点或者f节点没有被标记删除
if (f == null || f.value != f) // not already marked
//CAS操作将当前节点的next节点更换为new Node<K, V>(f),
//这里的new Node<K, V>(f)方法,其实就是一个标记节点
//这步操作完成后,原来:当前节点-->f 就变成了:当前节点-->new-->f,这个new是一个标记节点
casNext(f, new Node<K,V>(f));
else
//否则CAS操作把节点b的next由原来的节点n改变为f.next
b.casNext(this, f.next);
}
}
/**
* 返回节点的有效的值
* @return 如果该节点是标记节点或者原始链表头节点,直接返回null
*/ V getValidValue() {
Object v = value;
//如果该节点是标记节点或者原始链表头节点,直接返回null
if (v == this || v == BASE_HEADER)
return null;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v;
return vv;
}
/**
* 返回当前节点的快照
* @return new entry or null
*/ AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V> create Snapshot () {
Object v = value;
if (v == null || v == this || v == BASE_HEADER)
return null;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v;
return new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>(key, vv);
}
// UNSAFE mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long valueOffset;
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = Node.class;
valueOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("value"));
nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch ( Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
} 索引节点定义
/**
* Index nodes represent the levels of the skip list. Note that
* even though both Nodes and Indexes have forward-pointing
* fields, they have different types and are handled in different
* ways, that can't nicely be captured by placing field in a
* shared abstract class.
*/static class Index<K,V> {
//指向原始链表种的普通节点
final Node<K,V> node;
//指向下级索引节点
final Index<K,V> down;
//指向右边的索引节点
volatile Index<K,V> right;
/**
* 构造方法:创建一个索引节点
*/ Index(Node<K,V> node, Index<K,V> down, Index<K,V> right) {
this.node = node;
this. do wn = down;
this.right = right;
}
/**
* CAS设置右边的Index节点
*/ final boolean casRight(Index<K,V> cmp, Index<K,V> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, rightOffset, cmp, val);
}
/**
* 判断node节点是否已经删除
* @return true if indexed node is known to be deleted
*/ final boolean indexesDeletedNode() {
return node.value == null;
}
/**
* CAS设置一个新的后置节点newSucc
* @param 索引节点当前后置节点
* @param 新的后置节点
* @return true if successful
*/ final boolean link(Index<K,V> succ, Index<K,V> newSucc) {
Node<K,V> n = node;
newSucc.right = succ;
return n.value != null && casRight(succ, newSucc);
}
/**
* 跳过当前节点的后置节点
* @param succ 当前节点的后置节点
* @return true if successful
*/ final boolean unlink(Index<K,V> succ) {
return node.value != null && casRight(succ, succ.right);
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long rightOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = Index.class;
rightOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("right"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
} 头节点(头索引节点)定义
HeadIndex继承索引节点Index,多了一个level属性:
/**
* Nodes heading each level keep track of their level.
*/static final class HeadIndex<K,V> extends Index<K,V> {
final int level;
HeadIndex(Node<K,V> node, Index<K,V> down, Index<K,V> right, int level) {
super(node, down, right);
this.level = level;
}
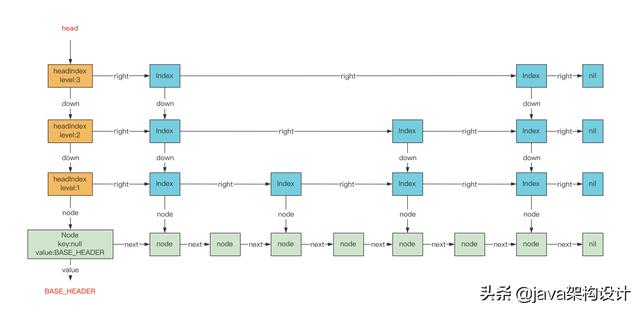
} 看了上面3种类型的节点定义,我们再画张图具化一下,让我们对这三种节点的定义更清晰一些:
接下来看看他的几个构造方法:
//空构造方法,默认采用key自带的Comparable实现
public ConcurrentSkipListMap() {
this.comparator = null;
initialize();
}
//指定comparator的构造方法
public ConcurrentSkipListMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
initialize();
}
//基于Map的构造方法,并将map中所有元素put进ConcurrentSkipListMap
public ConcurrentSkipListMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.comparator = null;
initialize();
putAll(m);
}
//基于SortedMap的构造方法,并将SortedMap中的所有元素put进ConcurrentSkipListMap
public ConcurrentSkipListMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
this.comparator = m.comparator();
initialize();
buildFromSorted(m);
} 这几个方法都调用了initialize()方法:
/**
* Initializes or resets state. Needed by constructors, clone,
* clear, readObject. and ConcurrentSkipListSet.clone.
* (Note that comparator must be separately initialized.)
*/private void initialize() {
keySet = null;
entrySet = null;
values = null;
descendingMap = null;
head = new HeadIndex<K,V>(new Node<K,V>(null, BASE_HEADER, null),
null, null, 1);
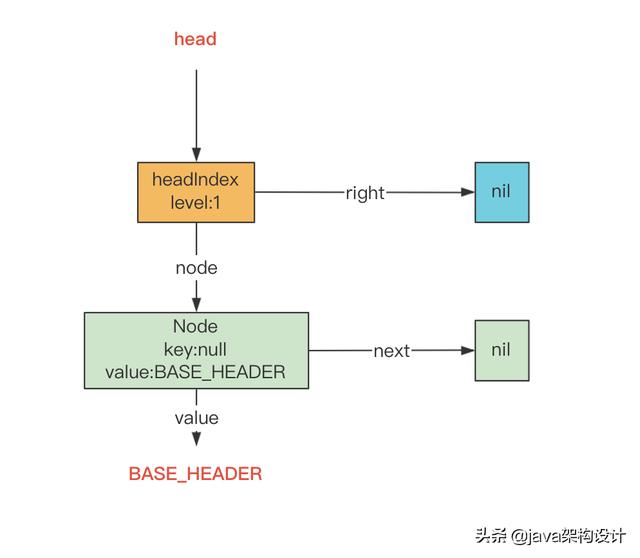
} initialize()方法会初始化keySet、entrySet、values、descendingMap这些属性字段为null,并将head指向一个初始化的头索引节点HeadIndex,initialize()执行后ConcurrentSkipListMap会形成如下的数据结构:
接下来我们基于这个初始化的ConcurrentSkipListMap来继续看doPut()、doRemove()、doGet()操作是如何进行的。
put操作
//对外提供的doPut操作
public V put(K key, V value) {
//不允许value为null
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//调用内部实现方法
return doPut(key, value, false);
} 进入内部实现doPut()方法:
/**
* Main insertion method. Adds element if not present, or
* replaces value if present and onlyIfAbsent is false.
* @param key the key
* @param value the value that must be associated with key
* @param onlyIfAbsent if should not insert if already present
* @return the old value, or null if newly inserted
*/private V doPut(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
Node<K,V> z; // added node
if (key == null)//不允许key为null
throw new NullPointerException();
//如果构造方法指定了排序方式则用指定的排序方式,否则采用key的排序方式
Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator;
outer: for (;;) {
//findPredecessor方法找到小于且最接近key值的节点b(首次即原始链表的头节点),n为b的next节点
for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) {
//如果b的后置节点不为空,需要处理后置节点,否则直接将z作为b的后置节点插入
if (n != null) {
Object v; int c;
Node<K,V> f = n.next;// 定义f作为n的后置节点,即:b-->n-->f
//如果此时n不等于b的后置节点了(可能有并发修改),则跳出当前循环,继续outer外层for循环
if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read(读不一致)
break;
//判断n是否已经被删除了
if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n is deleted
//让当前 线程 协助删除节点n,这个方法详情见上文原始链表普通节点定义源码中该方法的详细解释
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
//判断当前节点是否标记节点
if (b.value == null || v == n) // b is deleted
break;
//根据指定的cmp排序方式比较key和后置节点n的key大小并做交换
if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
//如果一样大
if (c == 0) {
//判断是否要覆盖掉或者设置值成功则直接返回vv
if (onlyIfAbsent || n.casValue(v, value)) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v;
return vv;
}
//上面的if不成功则跳出当前循环,继续寻找下一个最接近key值的节点
break; // restart if lost race to replace value
}
//理论上不会出现c < 0的情况,由findPredecessor保证
// else c < 0; fall through
}
//终于找到了要插入的位置了
z = new Node<K,V>(key, value, n);
//CAS操作插入 由b -> z 变成 b -> z -> n
if (!b.casNext(n, z))
break; // restart if lost race to append to b
//跳出外层outer循环
break outer;
}
}
//上面节点是插入了,接下来还要做索引节点的事情
int rnd = ThreadLocalRandom.nextSecondarySeed();//生成一个随机数
//0x80000001展开为二进制为10000000000000000000000000000001
//只有rnd为正偶数的情况下下面的代码才会成立
if ((rnd & 0x80000001) == 0) { // test highest and lowest bits
int level = 1, max;
//随机数(正偶数)从最低位的第二位开始,有几个连续的1则level就加几
while (((rnd >>>= 1) & 1) != 0)
++level;
Index<K,V> idx = null;
HeadIndex<K,V> h = head;
//如果随机出来的level没有超过当前最大层级数
if (level <= (max = h.level)) {
for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i)
//从第一级开始逐层向上创建索引节点,索引节点皆指向新插入的节点z
idx = new Index<K,V>(z, idx, null);
}
//如果level大于当前最大层级数
else { // try to grow by one level
//则让level等于最大层级数+1
level = max + 1; // hold in array and later pick the one to use
//定义一个idxs数组,用于记录每一层的索引节点
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Index<K,V>[] idxs =
(Index<K,V>[])new Index<?,?>[level+1];
//逐层向上创建索引节点,并存储idxs数组
for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i)
idxs[i] = idx = new Index<K,V>(z, idx, null);
//开始设置头节点
for (;;) {
h = head;
int oldLevel = h.level;
//如果头节点level大于等于新增节点的level,则跳出循环
if (level <= oldLevel) // lost race to add level
break;
//如果头节点level小于新增节点的level,则补充到新增节点的level
HeadIndex<K,V> newh = h;
Node<K,V> oldbase = h.node;
for (int j = oldLevel+1; j <= level; ++j)
newh = new HeadIndex<K,V>(oldbase, newh, idxs[j], j);
if (casHead(h, newh)) {
h = newh;
//此时的level变成了oldLevel
idx = idxs[level = oldLevel];
break;
}
}
}
// find insertion points and splice in
// 查找插入点并拼接,从旧的最高层级开始自旋
splice: for (int insertionLevel = level;;) {
int j = h.level;
//q为当前节点,r为右节点,t为目标节点的对应层级的索引节点
for (Index<K,V> q = h, r = q.right, t = idx;;) {
//如果遍历到了最右边,或者最下面,则跳出外层循环
if (q == null || t == null)
break splice;
//如果右索引节点存在
if (r != null) {
//右索引节点关联的普通节点
Node<K,V> n = r.node;
// compare before deletion check avoids needing recheck
//比较key的值和右索引节点关联的普通节点的key,按照指定的cmp
int c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key);
//如果n节点已经被标记为删除
if (n.value == null) {
//删除右节点,如果失败了,则从头再来
if (!q.unlink(r))
break;
//如果成功了,重新指向新的右节点
r = q.right;
continue;
}
//如果c>0,意味着需要继续向右移动一个索引节点继续重复上述操作
if (c > 0) {
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
//终于,找到了要插入的层级最右边了
if (j == insertionLevel) {
//在索引节点q、r之间插入索引节点t,q->r变成 q->r->t,失败了就从头再来
if (!q.link(r, t))
break; // restart
//如果t被标记删除了,那么调用findNode方法找到该节点,
//然后会调用里面的helpDelete方法来真正的删除该节点,并跳出循环
if (t.node.value == null) {
findNode(key);
break splice;
}
//向下一层继续链接索引节点,直至最底一层
if (--insertionLevel == 0)
break splice;
}
//j先自减,然后与insertionLevel以及level做比较
if (--j >= insertionLevel && j < level)
//t下移
t = t.down;
//q下移
q = q.down;
//r右移
r = q.right;
}
}
}
return null;
} 这里面还有一个关键的方法findPredecessor,按照指定的排序方式查找指定key的前置节点:
/**
* Returns a base-level node with key strictly less than given key,
* or the base-level header if there is no such node. Also
* unlinks indexes to deleted nodes found along the way. Callers
* rely on this side-effect of clearing indices to deleted nodes.
* @param key the key
* @return a predecessor of key
*/private Node<K,V> findPredecessor(Object key, Comparator<? super K> cmp) {
//key不允许null,大家平时编程也记得做一些防御性编程,对上下游要保持零信任
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException(); // don't postpone errors
//自旋
for (;;) {
//从头节点开始逐层往下、往右查找,q代表当前节点,r代表右节点,d代表down节点,
//这块就是典型的跳表查找方式
for (Index<K,V> q = head, r = q.right, d;;) {
if (r != null) {
Node<K,V> n = r.node;
K k = n.key;
//如果发现node节点被标记删除了,那么就协助删除它
if (n.value == null) {
if (!q.unlink(r))
break; // restart
r = q.right; // reread r
continue;
}
if (cpr(cmp, key, k) > 0) {
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
if ((d = q.down) == null)
return q.node;
q = d;
r = d.right;
}
}
} 至此,doPut方法的源码就解析完毕了,总结起来就是做了三件事情:
- 将目标数据节点z插入到原始链表中;
- 随机节点z的层级,并建立对应level的IndexNode;
- 从旧的最高层级开始自旋,将新建的IndexNode索引节点与其他索引节点通过右指针连接起来;
下面用图来演示这三步来加深一下理解,初始链表如下:
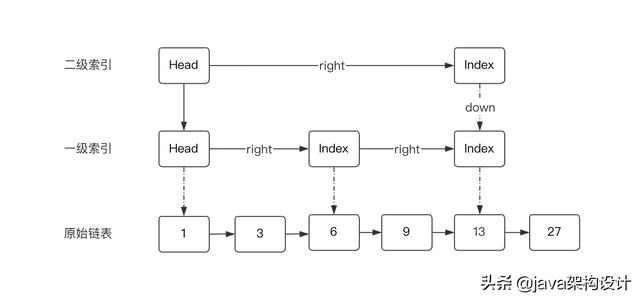
插入元素15,先找到小于15的最接近的数据节点,也就是13,然后从13开始往后遍历原始链表,找到插入的位置,也就是13和27之间:
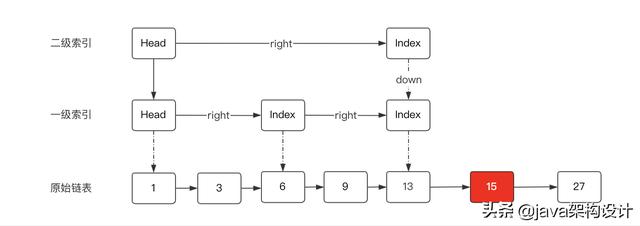
然后计算15这个节点的随机层级,假设随机层级为4,但是大于当前层级+1,因此就取3级,并建立索引节点,形成如下结构:
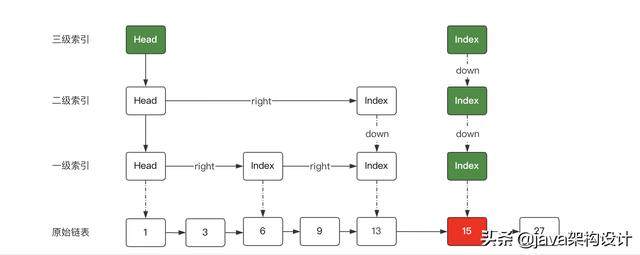
最后把每一个层级的right补齐,从head节点开始往右找当前层级,找到了就用right指针关联上,然后前一个索引下移,继续向右找目标索引,找到了13的二级索引,和右边的15节点的二级索引关联上,然后13的二级索引继续下移,向右找到节点15的一级索引并关联上:
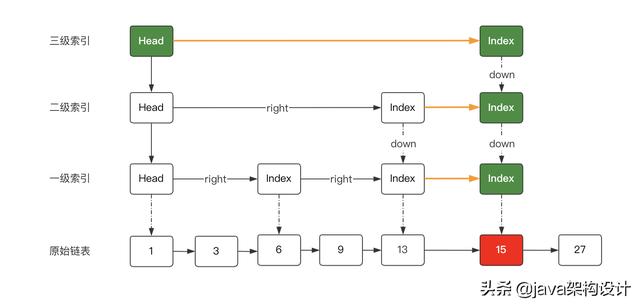
至此,一个新的节点15就成功地插入进去了,大家可以对照着图和源码一起解读。
remove操作
public V remove(Object key) {
return doRemove(key, null);
} 对外提供的方法remove用于删除指定的key,其调用了内部方法doRemove(Object key, Object value),我们进入doRemove方法解析一下它的源码:
/**
* Main deletion method. Locates node, nulls value, appends a
* deletion marker, unlinks predecessor, removes associated index
* nodes, and possibly reduces head index level.
*
* Index nodes are cleared out simply by calling findPredecessor.
* which unlinks indexes to deleted nodes found along path to key,
* which will include the indexes to this node. This is done
* unconditionally. We can't check beforehand whether there are
* index nodes because it might be the case that some or all
* indexes hadn't been inserted yet for this node during initial
* search for it, and we'd like to ensure lack of garbage
* retention, so must call to be sure.
*
* @param key 要删除的key
* @param value 如果不是null,必须和key映射的value一致
* @return 返回该节点,如果没找到则返回空
*/final V doRemove(Object key, Object value) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator;
//自旋
outer: for (;;) {
//根据指定的cmp找到key的前置索引节点,n作为b的右节点
for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) {
Object v; int c;
//如果n为null,说明key不存在,直接跳出外层循环
if (n == null)
break outer;
//如果存在,先定义一个f作为右节点的右节点
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
//不一致读,可能存在兵法修改,跳出当前循环,继续寻找前置节点
if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read
break;
//检查n是否被标记删除了,如果被删除了,协助删除节点n
if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n is deleted
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
//检查b是否被标记删除了
if (b.value == null || v == n) // b is deleted
break;
//比较key和n的key如果还小于(或大于,取决于cmp)n的key,说明前置节点找失败了,跳出外层循环,返回null
if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) < 0)
break outer;
//如果c > 0,继续向右找
if (c > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
//如果参数value不是null,并且和找到的v不相等,则跳出外层循环,返回null
if (value != null && !value.equals(v))
break outer;
//CAS操作将节点n的值设置为null,如果失败了,则跳出当前循环,继续查找最新的前置节点
if (!n.casValue(v, null))
break;
//在n和f之间增加标记节点,并将b指向f
if (!n.appendMarker(f) || !b.casNext(n, f))
findNode(key); // retry via findNode
else {
//清除索引节点
findPredecessor(key, cmp); // clean index
//如果头节点的右节点已经指向null了则减少level
if (head.right == null)
tryReduceLevel();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v;
return vv;
}
}
return null;
} 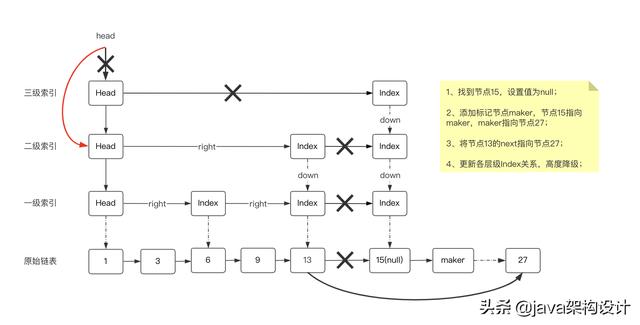
get操作
public V get(Object key) {
return doGet(key);
} 调用了内部方法doGet():
/**
* Gets value for key. Almost the same as findNode, but returns
* the found value (to avoid retries during re-reads)
*
* @param key the key
* @return the value, or null if absent
*/private V doGet(Object key) {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator;
outer: for (;;) {
for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) {
Object v; int c;
if (n == null)
break outer;
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read
break;
if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n is deleted
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
if (b.value == null || v == n) // b is deleted
break;
if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) == 0) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v;
return vv;
}
if (c < 0)
break outer;
b = n;
n = f;
}
}
return null;
} 这个方法的源码大家可以自己去看看,通过前面的分析,如果再看这个方法的代码就会觉得很简单了。
ConcurrentSkipListSet源码剖析
上面解析了ConcurrentSkipListMap的新增、删除、查找单个元素的源码以及ConcurrentSkipListMap整体的数据结构定义,我们乘胜追击,顺便看一下ConcurrentSkipListSet的源码,ConcurrentSkipListSet和ConcurrentSkipListMap的关系类似于HashSet和HashMap的关系,从它的构造方法就可以看出啦,它里面所有的操作都交给了ConcurrentSkipListMap来操作:
public class ConcurrentSkipListSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2479143111061671589L;
private final ConcurrentNavigableMap<E,Object> m;
public ConcurrentSkipListSet() {
m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E,Object>();
}
public ConcurrentSkipListSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E,Object>(comparator);
}
public ConcurrentSkipListSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E,Object>();
addAll(c);
}
public ConcurrentSkipListSet(SortedSet<E> s) {
m = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<E,Object>(s.comparator());
addAll(s);
}
/**
* For use by submaps
*/ ConcurrentSkipListSet(ConcurrentNavigableMap<E,Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
} 总结
读史可以明智,读源码可以让我们写出更好的代码,通过对ConcurrentSkipListMap源码的解读,我们至少学会了以下这些知识点:
- 了解掌握Map家族成员的整体结构;
- 对ConcurrentSkipListMap的底层实现机制跳表数据结构的掌握;
- ConcurrentSkipListMap是一个有序的且并发安全的Key-Value集合;
- ConcurrentSkipListSet是基于ConcurrentSkipListMap实现的针对其Key的一个有序的且并发安全的集合;
进一步学习:
- 实际开发中哪些业务场景能应用ConcurrentSkipListMap?
- TreeMap为什么用红黑树来实现的?
- 尝试阅读Redis中的SortedSet的实现源码。
欢迎大家在评论区交流,一起学习,共同成长~


