TreeMap
简介
TreeMap是一个直接由 红黑树 实现的结构,对于Key值得比较来排序,显然得到:
1.key的class必须实现comparable方法, 不能抛出ClassCastException异常,否则必须指定一个comprartor
2.由于TreeMap实现了Serializable接口,所以默认的或者自定义的comparator也应该实现该接口
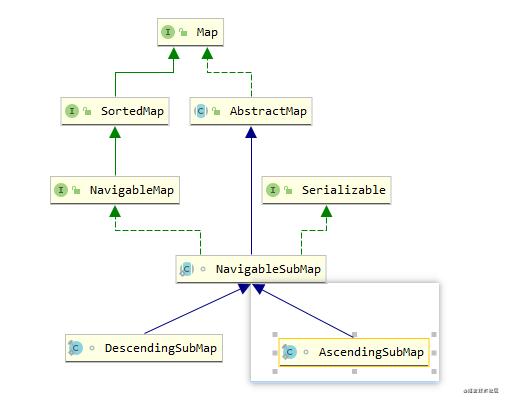
最重要的是,实现了NavigableMap,我理解为导航map,提供了各种操作map视图的操作
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends Abstract Map<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java .io.Serializable{}
复制代码
构造方法
四个构造方法,其实就是是否使用默认的compatator
对于无序Map,直接调用putAll,有序的SortedMap话递归调用buildFromSorted,提高效率
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
复制代码
但是putAll依然判断了map instanceof SortedMap
具体的红黑树的操作在此不作赘述
remove(),put()最根本的操作是红黑树的操作,get()也是二叉搜索树比较直观的实现
方法详解
- 有关树的操作的方法,其实就是代码分支比较多,需要考虑各种情况然后转换为代码就好了
- 比较的话看如果有comparator就用,没有就用key默认的comparable
successor() 查找下个节点
- 在containsValue()从第一个节点开始successor遍历
- 在 forEach ()从第一个节点开始successor遍历
- replaceAll()从第一个节点开始successor遍历赋值新的value
- remove()遍历找出Object删除
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
// 首先明确,下个节点是比当前节点大的节点,为当前节点右节点的左叶子节点
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
// 当右节点为空,并且是父节点的右节点时,下个节点当前分支树的父节点
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
// 当右节点为空,并且是父节点的左节点时,下个节点当前节点的父节点
return p;
}
}
复制代码
getCeilingEntry()/getFloorEntry 获取[low,key]/[key,high]的最大/小值,没有返回null
// 这个跟successor是相似的,其实如果根据搜索树没找到,就是找的下一个节点
final Entry<K,V> getCeilingEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
//比当前节点小,再跟左子节点比较
if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
else
return p;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
//比当前节点大,再跟右子节点比较
if (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
} else {
//这里跟successor相同,比最右叶子大,下一个为当前子树的父节点
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
} else
//相等的话返回当前节点
return p;
}
return null;
}
//跟上面是镜像的过程
final Entry<K,V> getFloorEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
//比当前节点大,跟右子节点比较
if (cmp > 0) {
if (p.right != null)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
} else if (cmp < 0) {
//比当前节点小,再跟左子节点比较
if (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
//比最左叶子小,下一个为当前子树的父节点
while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
} else
//相等的话返回当前节点
return p;
}
return null;
}
复制代码
getHigherEntry()/getLowerEntry获取[low,key)/(key,high]的最大/小值,没有返回null
跟getCeilingEntry一样的只不过对于相等的情况,不考虑相等的情况
final Entry<K,V> getHigherEntry(K key) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = compare(key, p.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
if (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
else
return p;
} else {
if (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
} else {
Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = p;
while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) {
ch = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
}
return null;
}
复制代码
DescendingMap()翻转map
底层由DescendingSubMap()实现,其实还是这个map,只不过对于所有的操作,比如getfist(),会将其转换为getLast()来执行,所以对于DescendingMap()的操作依然会影响原Map
同样的,subMap()的操作也会影响原Map
static final class DescendingSubMap<K,V> extends NavigableSubMap<K,V> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 912986545866120460L;
// m是当前Map,fromStart是否从头开始为ture则lo为null,lo开始位置,loInclusive是否包含开始位置
DescendingSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m,
boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive,
boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) {
super(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive);
}
复制代码
//DescendingSubMap一些方法的实现
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest() { return absHighest(); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest() { return absLowest(); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key) { return absFloor(key); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key) { return absLower(key); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key) { return absCeiling(key); }
TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key) { return absHigher(key); }
复制代码
subMap()+headMap()+tailMap()
正常map调用的是AscendingSubMap,跟DescendingMap相同,只是相反的实现