八大数据结构
1、什么是数据结构?
数据结构是以某种特定的布局方式存储数据的容器;
2、为什么需要数据结构?
数据是计算机科学当中最关键的实体,而数据结构则可以将数据以某种组织形式存储;
3、常见的数据结构包含?
数组、链表、队列、栈、哈希表、树、堆和图;
数组
数组(Array):有序表,有序的元素序列;
数组在内存中占一片连续的存储区;C语言中规定,数组名就代表了该数组的首地址;
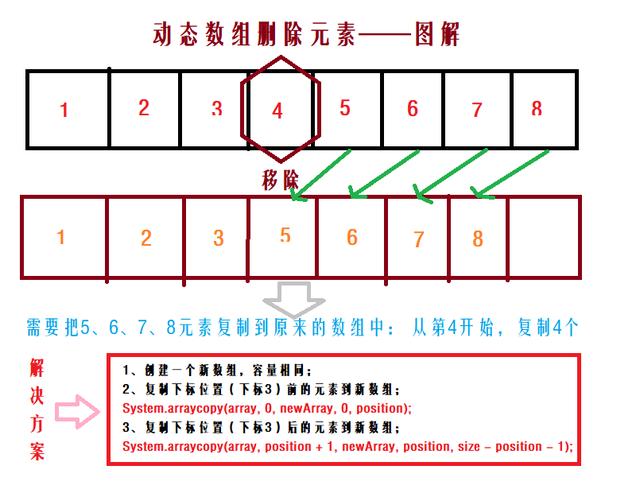
动态数组
动态数组:在声明时没有确定数组大小的数组,当要用它时可重新指出数组的大小;
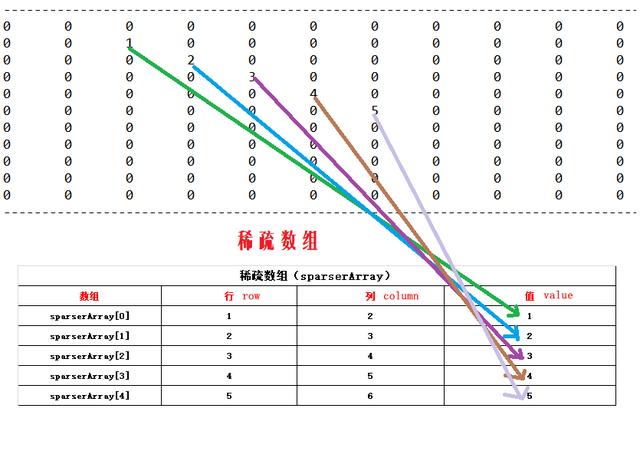
稀疏数组
稀疏数组(Sparse Array):一种只为数组中的非零元素分配内存的特殊类型数组,内存中存储了稀疏数组中非零元素的下标和值。
案例:动态数组
package com.what21.structure.array.dynamic.case01.mode01;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class DynamicArrayList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
// 扩容因子
private double capacityFactor;
private T[] data;
private int size = 0;
public DynamicArrayList() {
this(10, 1.5);
}
public DynamicArrayList(int size, double capacityFactor) {
this.capacityFactor = capacityFactor;
this.init(size);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void init(int size) {
if (size >= 0) {
data = (T[]) new Object[size];
} else {
data = (T[]) new Object[10];
}
}
/**
* 检查扩容
*/
private void checkCapacity() {
if (size > data.length - 1) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] capacityData = (T[]) new Object[(int) (data.length * this.capacityFactor)];
System.arraycopy(this.data, 0, capacityData, 0, this.data.length);
this.data = capacityData;
}
}
/**
* 容器大小
*
* @return
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* 添加元素
*
* @param t
*/
public void add(T t) {
this.checkCapacity();
this.data[size++] = t;
}
/**
* 获取元素
*
* @param index 下标
* @return
*/
public T get(int index) {
T t = null;
if (index >= 0 && index < data.length) {
t = data[index];
}
return t;
}
/**
* 移除元素
*
* @param t
*/
public void remove(T t) {
if (t == null) {
return;
}
int operateIndex = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < this.size(); i++) {
if (t.equals(data[i])) {
operateIndex = i;
}
}
if (operateIndex > -1) {
removeByIndex(operateIndex);
}
}
/**
* 添加元素
*
* @param t
*/
public T removeByIndex(int index) {
// 检查范围
if (index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
return null;
}
T t = this.data[index];
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] arrayData = (T[]) new Object[size];
System.arraycopy(this.data, 0, arrayData, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(this.data, index + 1, arrayData, index, size - index - 1);
this.data = arrayData;
size--;
return t;
}
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new DynamicArrayListIterator<T>(this.data, this.size);
}
// ===========================================================================//
// === java.util.Iterator
// ===========================================================================//
@SuppressWarnings("hiding")
private class DynamicArrayListIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
private T[] data;
private int size;
private int cursor = 0;
public DynamicArrayListIterator(T[] data, int size) {
this.data = data;
this.size = size;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (this.data == null) {
return false;
}
if (this.cursor < this.size) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public T next() {
return this.data[this.cursor++];
}
}
// ===========================================================================//
// === The end
// ===========================================================================//
}
package com.what21.structure.array.dynamic.case01.mode01;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class DynamicArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义动态数组
DynamicArrayList< Integer > intList = new DynamicArrayList<Integer>();
// 初始化动态数组
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
intList.add(i);
}
// 打印动态数组
System.out.println("普通的for循环访问数组:");
System.out.println("数组的元素共有:" + intList.size());
for (int i = 0; i < intList.size(); i++) {
System.out.printf("%d ", intList.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
printSeparator();
// 操作动态数组
int removeValue = intList.removeByIndex(9);
System.out.println("删除元素值:" + removeValue);
intList.remove(27);
System.out.println("删除元素值:" + 27);
intList.add(97);
System.out.println("添加元素值:" + 97);
intList.add(199);
System.out.println("添加元素值:" + 199);
printSeparator();
// 打印动态数组
// 使用增强的for循环,需要实现java.lang.Iterable接口;
System.out.println("增强的for循环访问数组:");
System.out.println("数组的元素共有:" + intList.size());
for (Integer value : intList) {
System.out.printf("%d ", value);
}
System.out.println();
printSeparator();
// 迭代器
System.out.println("迭代器遍历数组:");
Iterator<Integer> intIterator = intList.iterator();
while (intIterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.printf("%d ", intIterator.next());
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* @param array
*/
static void printSeparator() {
for (int i = 0; i < 45; i++) {
System.out.printf("%s", "--");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
案例:稀疏数组
package com.what21.structure.array.sparser.case01.mode01;
public class SparserArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 11行11列
int[][] towDimensionArray = new int[11][11];
for (int i = 0; i < towDimensionArray.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < towDimensionArray[0].length; j++) {
towDimensionArray[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// 赋值
towDimensionArray[1][2] = 1;
towDimensionArray[2][3] = 2;
towDimensionArray[3][4] = 3;
towDimensionArray[4][5] = 4;
towDimensionArray[5][6] = 5;
System.out.println(" 二维数组 :");
iterate(towDimensionArray);
// 转稀疏数组
int[][] sparserArray = toSparserArray(towDimensionArray);
System.out.println("二维数组转稀疏数组:");
iterate(sparserArray);
System.out.println("稀疏数组转二维数组:");
int[][] convertedTwoDimensionArray = toTwoDimension(11, 11, sparserArray);
iterate(convertedTwoDimensionArray);
}
/**
* @param row 行
* @param column 列
* @param sparserArray 稀疏数组
* @return
*/
private static int[][] toTwoDimension(int rows, int column, int[][] sparserArray) {
int[][] twoDimensionArray = new int[rows][column];
if (twoDimensionArray == null || twoDimensionArray.length <= 0) {
return twoDimensionArray;
}
// 为二维数组赋值
for (int i = 0; i < sparserArray.length; i++) {
int rowSubscript = sparserArray[i][0];
int columnSubscript = sparserArray[i][1];
int value = sparserArray[i][2];
twoDimensionArray[rowSubscript][columnSubscript] = value;
}
return twoDimensionArray;
}
/**
* @param towDimensionArray
*/
static int[][] toSparserArray(int[][] towDimensionArray) {
// 第一步,求出有多少有效个数据
int rows = 0;
for (int[] oneDimensionArray : towDimensionArray) {
for (int value : oneDimensionArray) {
if (value > 0) {
rows++;
}
}
}
// 第二步:创建稀疏数组
int[][] sparserArray = new int[rows][3];
// 第三步:为稀疏数组赋值
int sparserArrayRows = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < towDimensionArray.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < towDimensionArray[i].length; j++) {
int value = towDimensionArray[i][j];
if (value > 0) {
sparserArray[sparserArrayRows][0] = i;
sparserArray[sparserArrayRows][1] = j;
sparserArray[sparserArrayRows][2] = value;
sparserArrayRows++;
}
}
}
return sparserArray;
}
/**
* @param array
*/
static void iterate(int[][] array) {
if (array == null || array.length <= 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 45; i++) {
System.out.print("--");
}
System.out.println();
// 打印
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array[i].length; j++) {
System.out.printf("%dt", array[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 45; i++) {
System.out.printf("%s", "--");
}
System.out.println();
}
}


